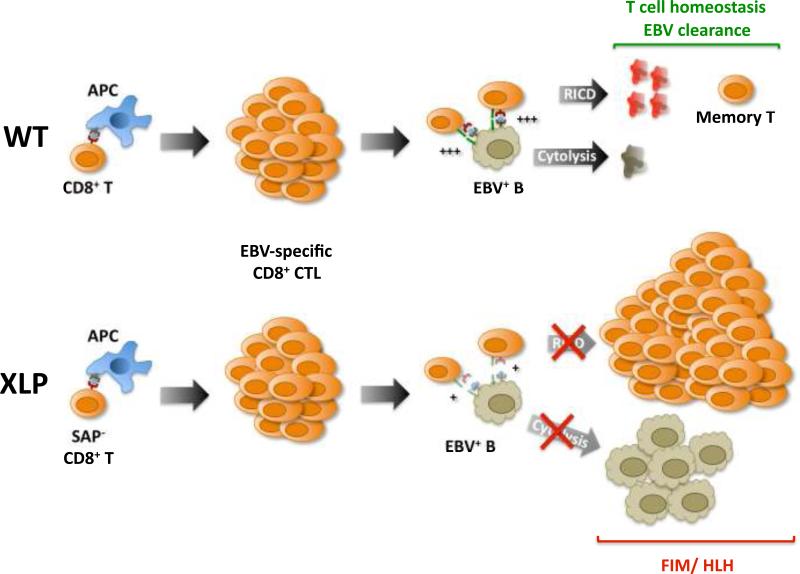
Fig. 3. Impaired RICD of SAP-deficient CD8+ T cells contributes to EBV-induced FIM in XLP patients.
In normal individuals (WT), primary EBV exposure primes a robust CD8+ T-cell response to viral antigens. EBV-specific CTLs can strongly conjugate with and lyse EBV+ B lymphoblasts, helping to clear almost all virally infected cells. The relatively strong TCR restimulation signal (+++) received from this encounter triggers RICD and helps maintain T-cell homeostasis. In XLP patients, CTL generation proceeds normally, but ablation of SAP results in poor T-B conjugation, impaired cytotoxic elimination of EBV-infected B cells, and weak TCR restimulation (+) that fails to induce RICD. Consequently, unchecked expansion of both EBV+ B lymphoblasts and activated CD8+ T cells can give rise to fatal EBV-induced FIM/HLH.