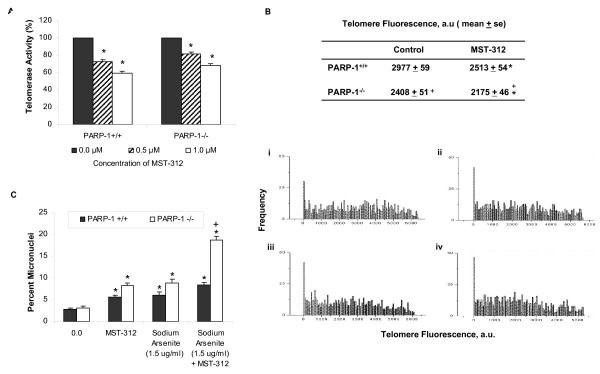
Figure 5.
Telomerase inhibition in PARP-1 deficient MEFs reduced telomere length and increased genomic instability. (A) Measurement of telomerase activity in PARP-1+/+ and PARP-1-/- MEFs with untreated controls (black columns), 0.5 μM (striped columns) and 1.0 μM (white columns) of MST-312 for 72 hours. (B) Telomere length frequency distribution in (i) PARP-1+/+ MEFs (ii) PARP-1-/- MEFs (iii) PARP-1+/+ MEFs with MST-312 and (iv) PARP-1-/- MEFs with MST-312. Telomerase inhibition in PARP-1 deficient MEFs resulted in greatest decrease in telomere length. (C) Histogram of micronuclei formation in PARP-1+/+ MEFs (black columns) and PARP-1-/- MEFs (white columns) with sodium arsenite and MST-312 treatment. MN frequency was significantly increased in telomerase inhibited PARP-1 deficient MEFs following exposure to 1.5 μg/μl of sodium arsenite. Error bars indicate standard error between three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 compared with respective untreated controls. +p < 0.05 compared between MST-312 treated cells with or without arsenite treatment.