Figure 5.
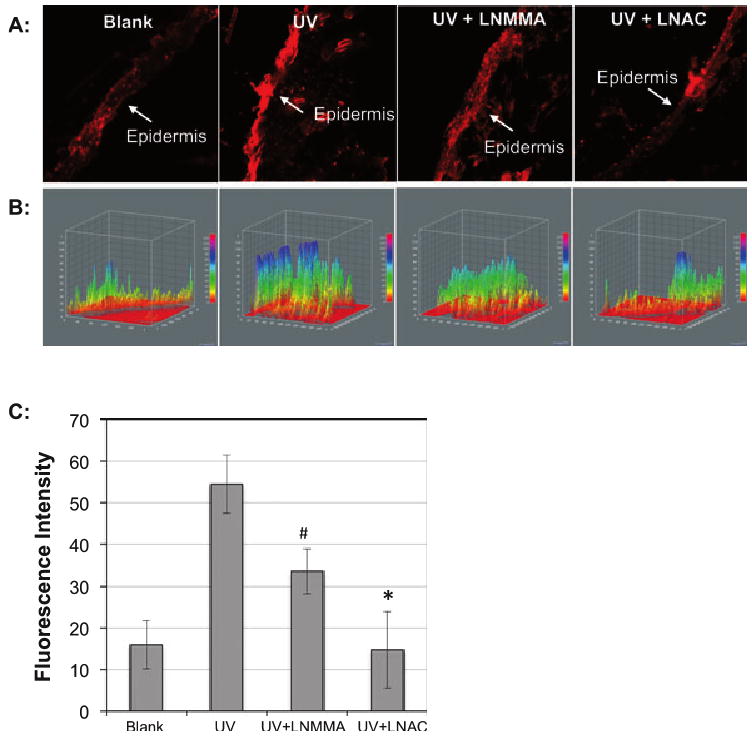
PI staining was used to determine the UVB-induced injury of skin tissue of mice. The mice were injected intraperitoneally with l-NMMA (10 mg kg−1) or l-NAC (500 mg kg−1) at 1 h before UVB irradiation. Immediately after irradiation, the mice were injected subcutaneously with 0.1 mL PI (100 μg mL−1) and the skin tissues were collected at 30 min postirradiation. The images of the skin sections were captured by fluorescence microscope. (A) Images of the PI-stained skin slices. (B) A 3-D analysis of the fluorescence intensity of the PI staining skin tissue using ImageJ (v1.34k; NIH). The fluorescence intensity is analyzed against distance of the slice in two dimensions. (C) The average fluorescence intensity of three measurements. #P < 0.01 vs UVB alone; *P < 0.02 vs UVB alone.
