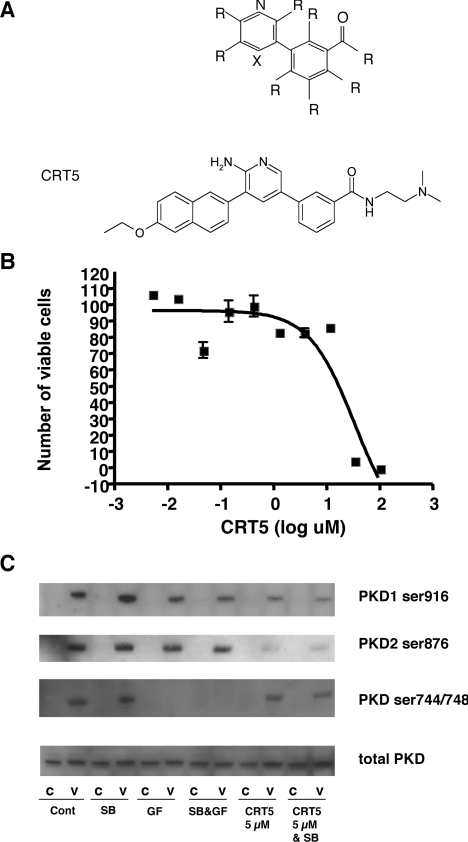
Figure 1. Structure, toxicity and specificity of CRT5.
(A) Core structure of PKD pyridine benzamide (upper panel) and pyrazine benzamide inhibitors, where R indicates one of several different functional groups, and X is either a nitrogen (N) or carbon covalently linked to a functional group (C–R). Further details of the structure of these compounds are provided in [18]. The structure of CRT5 is shown in the lower panel. (B) HUVECs were incubated with CRT5 (5 nM–100 μM) for 24 h. Cell viability was estimated by an MTT-based assay and plotted against the log CRT5 concentration. Non-linear regression analysis was used to determine the LD50 value. (C) Confluent HUVECs were pre-incubated for 30 min with vehicle (Cont; 0.1% DMSO), 5 μM SB203580 (SB), 3 μM GF109203X (GF), 5 μM SB203580 plus 3 μM GF109203X (SB&GF) or 5 μM CRT5 with and without 5 μM SB203580 (CRT5&SB and CRT5 respectively) as indicated. This was followed by 10 min stimulation with vehicle (C) or 25 ng/ml VEGF (V). Cell lysates were immunoblotted and probed with antibodies against phospho-PKD1 (Ser916 or Ser744/Ser748), phospho-PKD2 (Ser876) or total PKD as indicated.