Figure 2.
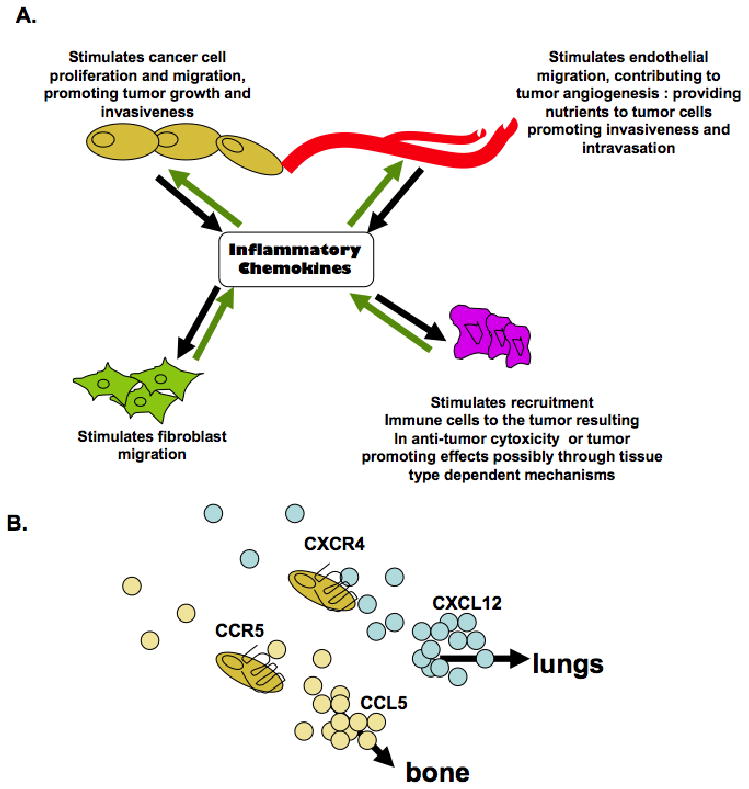
Model for the functional roles of inflammatory chemokinesignaling in cancer. (A) Stromal and epithelial cells secrete inflammatory chemokines, contributing to the bioavailability of chemokinesin the local tisuemicroenvironment. Inflammatory chemokinesregulate autocrineand paracrinesignaling interactions between stromal and epithelial cells to regulate cellular proliferation, migration and invasion. (B) Expression of Inflammatory chemokinesin normal tissues, as demonstrated by CXC112 and CCL5 create a chemokinegradient which regulate homing of chemokinereceptor expressing cancer cells to other organs.
