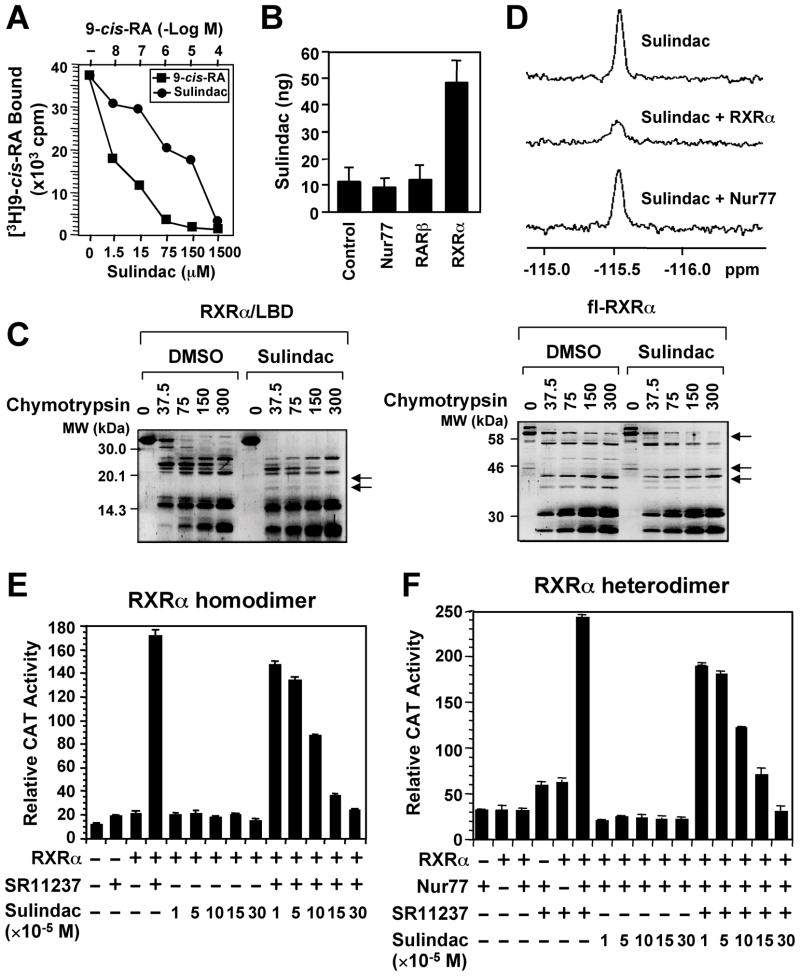
Figure 1. Sulindac Binds to RXRα.
(A) Sulindac binding to RXRα in vitro. RXRα LBD protein was incubated with [3H]9-cis-RA in the presence or absence of Sulindac or unlabeled 9-cis-RA. Bound [3H]9-cis-RA was quantitated by liquid scintillation counting.
(B) Sulindac binding to RXRα in cells. HEK293 cells stably expressing RXRα, Nur77 or RARβ were treated with 100 μM sulindac for 3 hr. The same amount of purified RXRα, Nur77, or RARβ protein was subjected to HPLC analysis for the presence of Sulindac.
(C) Altered sensitivity of RXRα LBD or GST-RXRα to chymotrypsin (μg/ml) by Sulindac (100 μM).
(D) Comparison of 19F NMR spectra of Sulindac (100 μM) in the absence and presence of 10 μM RXRα LBD or Nur77 protein.
(E, F) Sulindac inhibits transactivation of RXRα homodimers and heterodimers. (TREpal)2-tk-CAT (Zhang et al., 1992a) (E) or βRARE-tk-CAT (Zhang et al., 1992b) (F), Nur77 and/or RXRα were transiently transfected into CV-1 cells. Cells were treated with or without SR11237 (10−6 M) in the presence or absence of Sulindac. CAT activity was determined.
One of three to five similar experiments is shown. Error bars represent SEM.
See also Figure S1.