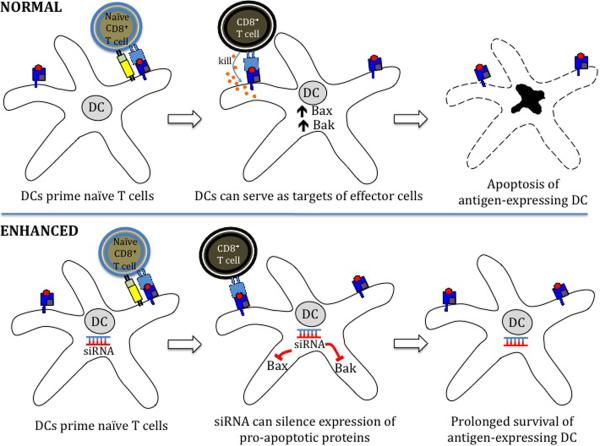
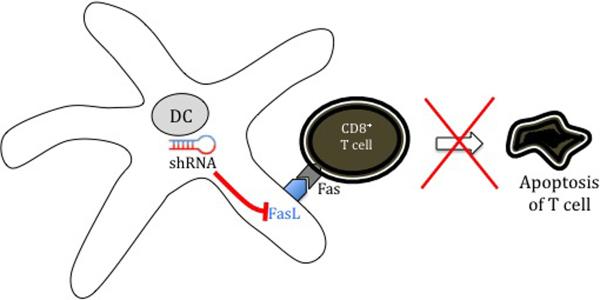
Figure 3.
Strategies to improve DC-T cell interaction in enhancing therapeutic DNA vaccine potency. (A) Prolonging DC survival. Once DCs have primed naïve T cells, they can become the target of these effector T cells. The use of short interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting key pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bak and Bax can transiently silence expression of Bak and Bax, improving DNA-transfected DC resistance to apoptosis and improving DC-T cell interaction. (B) Prevention of activated CD8+ T cell apoptosis. The Fas ligand (FasL) found on the surface of DCs is a pro-apoptotic signalling protein that binds to the Fas receptor on T cells, causing them to undergo apoptosis. Creation of DNA encoding small hairpin RNA (shRNA) to block FasL can prevent apoptosis of activated T cells and improve DC-T cell interaction.