Figure 3.
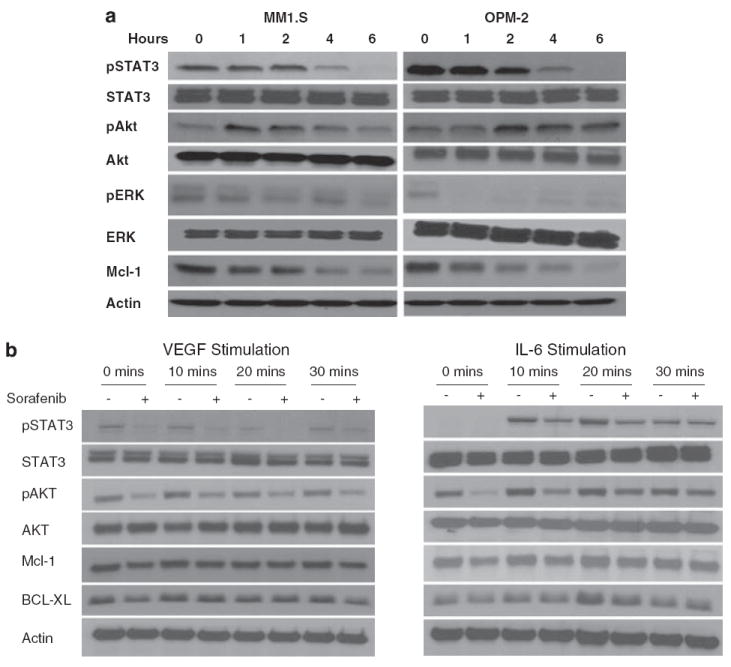
Sorafenib treatment induces changes in proliferation and survival signals in multiple myeloma (MM) cells. Immunoblots of extracts from MM1.S and OPM2 cells treated with sorafenib (5 μm) for the indicated time periods show consistent downregulation of phospho-ERK, phospho-STAT3 and Mcl-1 (a). In contrast a time-dependent increase in Akt phosphorylation was observed that returned to near baseline levels by 6 h of treatment. No change was observed in total Akt, Erk or Stat3. Equal protein loading is confirmed by blotting for actin (a). MM1.S cells were then incubated with Interleukin-6 (IL-6) (25 ng/ml) or VEGF (50 ng/ml) for the indicated times with (+) or without a 6 h pre-incubation with sorafenib (5 μm) (b). IL-6 and VEGF treatments were carried out during the last 30, 20 or 10 min of the 6-h incubation with the drug as shown in the figure. Immunoblots were performed for pSTAT3, pAKT, MCl-1, BCl-xl, total STAT3, AKT and β-actin (control). Preincubation with sorafenib partially abrogates the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and IL-6-induced upregulation of pSTAT3 as well as Mcl1. MM1.S cells were treated with sorafenib (5 μm) for 4, 8 or 24 h, cells harvested, and subjected to gene expression profiling using Affymetrix U 133 Plus 2.0 platform (c). The experiment was repeated three times and the corresponding samples were combined to reduce experiment to experiment variation. The output files were imported into Genespring 7.2, GCRMA normalized and expression levels analysed at each time point. The graph and the accompanying table show genes that show a consistent time-dependent differential regulation.

