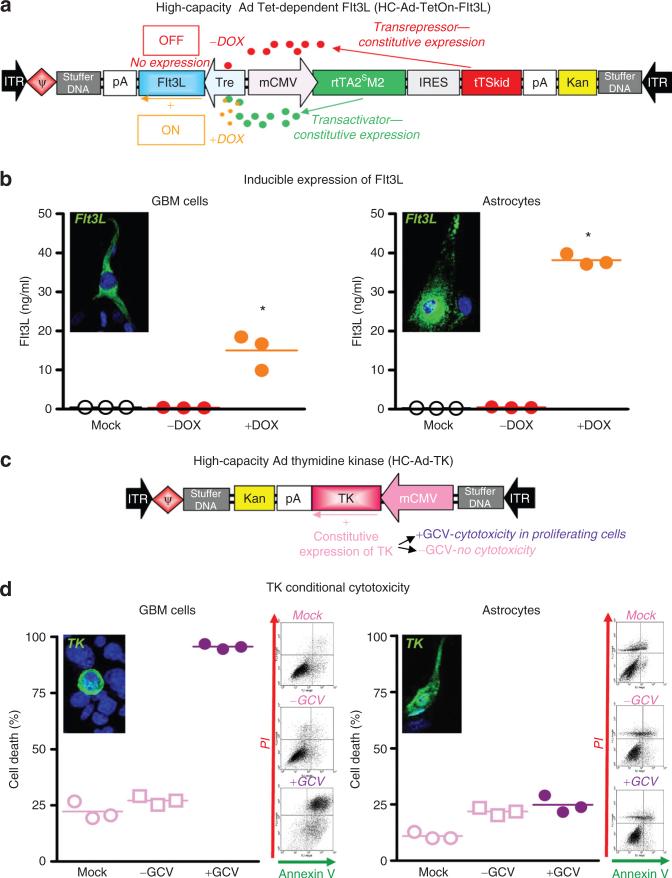
Figure 1.
Structure and in vitro characterization of therapeutic HC-Ads. (a) Structure and transcriptional regulation of HC-Ad-TetOn-Flt3L. (b) CNS-1 GBM cells and astrocytes in primary culture were infected with HC-Ad-TetOn-Flt3L with or without the inducer, DOX. Flt3L expression was assessed by immunofluorescence and ELISA. *P < 0.05 vs. mock infection. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test. (c) Illustration depicting structure and function of HC-Ad-TK. (d) CNS-1 GBM cells and astrocytes in primary culture were infected with HC-Ad-TK and incubated with or without the prodrug GCV. TK expression was assessed by immunofluorescence, and cell death was determined by flow cytometric analysis of Annexin V/PI-stained cells. *P < 0.05 vs. mock infection. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; DOX, doxycycline; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Flt3L, fms-like tyrosine kinase ligand 3; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme; GCV, ganciclovir; HC-Ad, high-capacity adenovirus; PI, propidium iodide; TK, thymidine kinase.