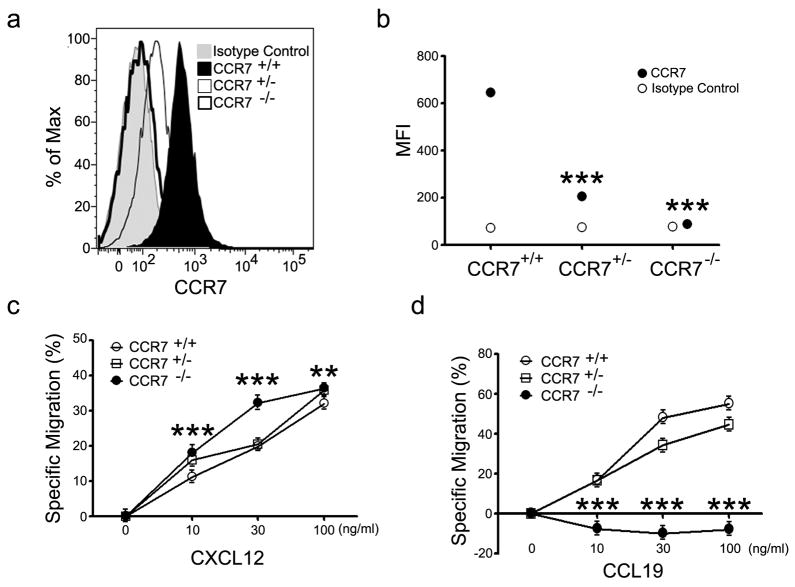
Figure 5.
Comparison of Ccl19 triggered chemotaxis of B cells from wild type, Ccr7+/−, and Ccr7−/− mice. (a) CCR7 expression on wild type and mutant mice. Flow cytometry with an isotype control and CCR7 antibody. Spleens B cells were purified from wild type, Ccr7+/−, and Ccr7−/− mice. Results are representative of 4 experiments done. (b) Mean Fluorescent intensity (MFI) of CCR7 expression on B cells from wild type and mutant mice. Data representative of one of four experiments performed. Statistical significance was calculated using Mann-Whitney t-test compared with MFI of CCR7 of CCR7+/+. (***, p<0.0001) (c) CXCL12 mediated Chemotaxis. A standard chemotaxis assay was performed with splenic B cells. The results are mean and standard error of sextuplet samples from one experiment and are shown as % specific migration. A standard chemotaxis assay was performed with splenic B cells. Results are representative of one of 3 experiments performed. Statistical significance was calculated using Mann-Whitney t-test compared with CCR7+/+. (**, p<0.01 and ***, p<0.001) (d) CXCL19 mediated chemotaxis. The Results are mean and standard error of sextuplet samples from one experiment and are shown as % specific migration. Results are representative of one of 3 experiments performed. Statistical significance was calculated using Mann-Whitney t-test compared with CCR7+/+. (***, p<0.001)