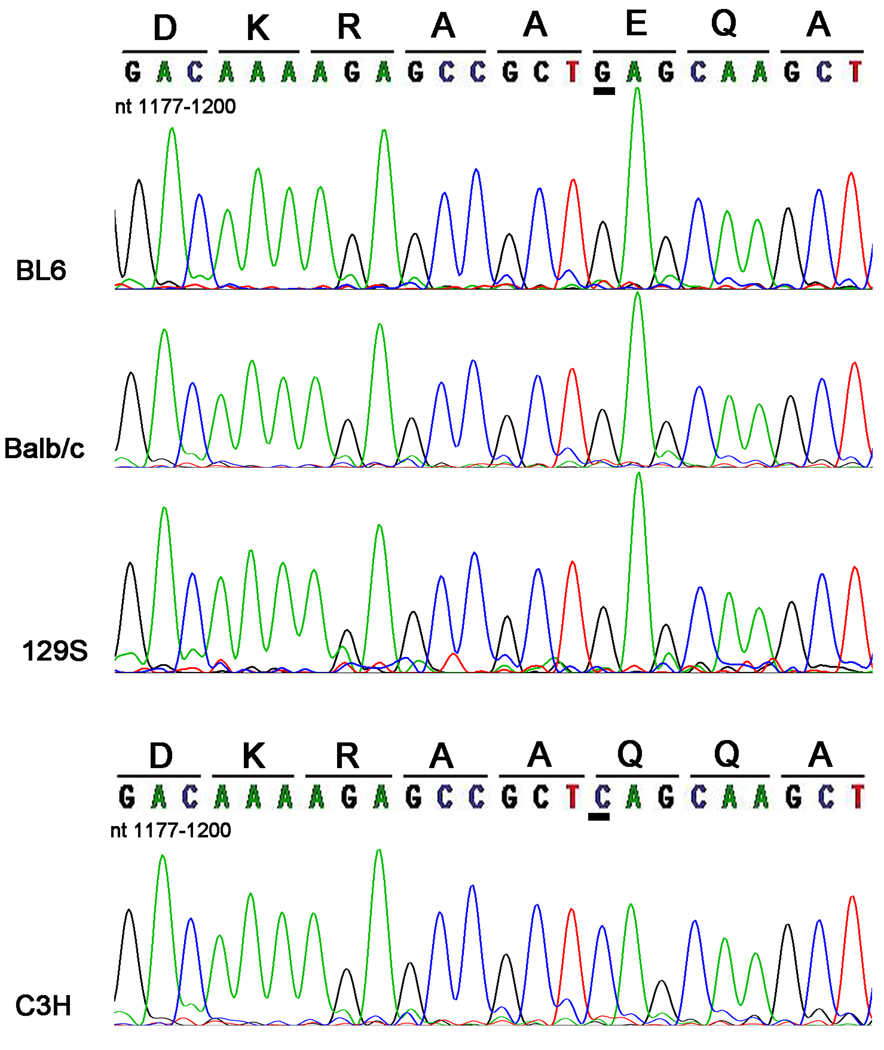
Figure 4.
Discovery of a novel endogenous parkin mutation in C3H mice. RT-PCR was performed using total RNA that was extracted from cerebral cortical tissues of BL6, Balb/c, C3H, and 129S mice. The amplified PCR products spanned bases 895–1395 of the mouse parkin cDNA sequence. The PCR products were sequenced and analyzed for mutations. The image shows the respective portion (nucleotide bases 1177–1200) of sequencing electropherogram for the various mouse strains. The corresponding amino acid sequences are written above the respective DNA codons. A novel endogenous G1192C parkin cDNA mutation was identified in C3H mice. This mutation translates into a missense E398Q mutation. The 1192 cDNA residue is underlined in order to highlight the location of the novel G1192C mutation in the mouse parkin cDNA sequence.