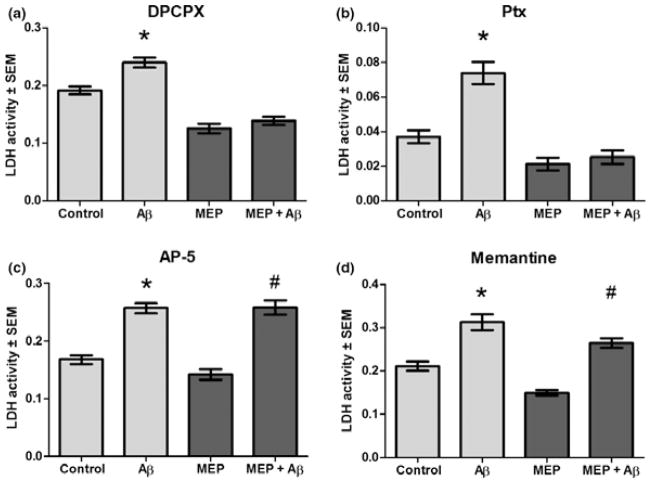
Fig. 2.
MEP-induced neuroprotection against Aβ: NMDAR antagonists abolished protection but antagonism of adenosine A1 receptors or Gi/o protein-coupled receptors had no effect. MEP of cerebellar cultures (as in Fig. 1) was performed with the respective receptor antagonists present for the first 3 days in a 6-day protocol, followed by 25 μM Aβ25–35 or vehicle for 24 h and media LDH assays. (a) dipropylxanthine (DPCPX) (100 nM), adenosine A1 receptor antagonist, did not prevent MEP neuroprotection. (b) Pertussis toxin (Ptx, 50 ng/mL), Gi/o protein-coupled receptor antagonist, also did not alter MEP neuroprotection. (c) AP-5 (45 μM), NMDAR antagonist, completely abolished MEP neuroprotection. (d) Memantine (50 μM), NMDAR antagonist, significantly inhibited MEP neuroprotection. *p < 0.001 versus control; #p < 0.001 versus MEP; 1-way ANOVA with Scheffe post hoc test (n = 6).