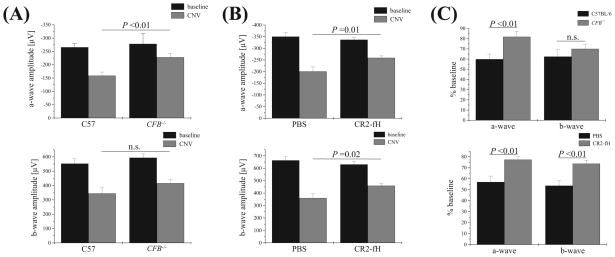
Figure 3.
CNV and retina function in CR2-fH–treated and fB-deficient mice. ERG recordings were performed before laser photocoagulation (baseline) and at the end of the experiment (after 6 days of CNV) using single-flash ERG recordings at a single light intensity of 2.48 photopic cd · s/m2. (See Figure 1 for ERG traces from wt, C57BL/6 animals.) ERG responses were analyzed from (A) CFB+/+ and CFB−/− mice and (B) wt mice treated with either PBS or CR2-fH. (A) A-wave and b-wave amplitudes at baseline were identical for CFB+/+ and CFB −/− mice. However, after CNV induction, a genotype-dependent difference was identified. CFB+/+ mice exhibited a significant loss of ERG amplitudes after CNV, whereas ERG amplitudes were relatively preserved in CFB−/− mice. (B) Reductions in ERG a- and b-wave amplitudes were significantly lower in mice treated intravenously with CR2-fH (250 μg on days 0, 2, and 4 after laser injury) compared with PBS-treated mice. (C) Summary of ERG data showing ERG a-waves as percentage of baseline amplitudes for the CFB+/+ and CFB−/− and the PBS and CR2-fH comparisons.