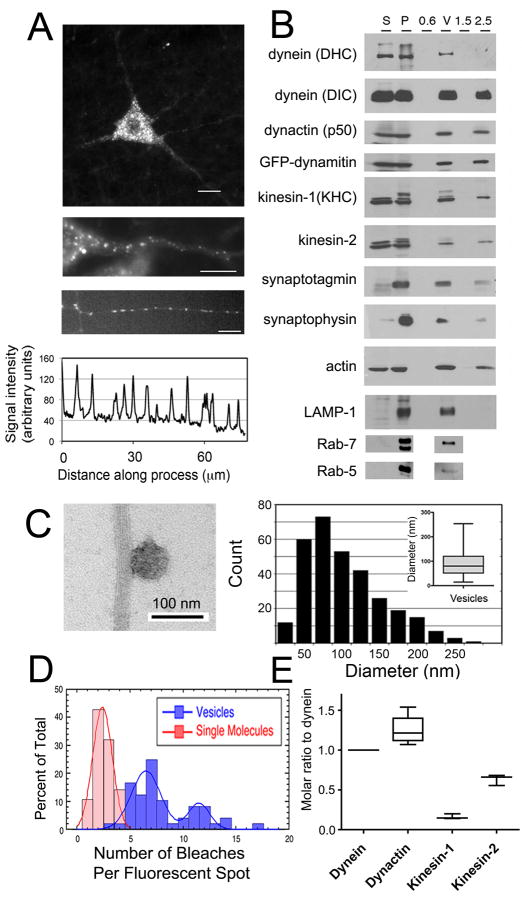
Fig. 1. MT motor proteins dynein and kinesin co-purify with axonal transport vesicles and drive active motility in vitro.
(A) Top, GFP-dynamitin is distributed in a punctate pattern throughout the cell soma and processes of motor neurons in vivo. Middle, GFP-dynamitin is localized to vesicles distributed along the axon of a motor neuron in vivo. Bottom, GFP-dynamitin is distributed to vesicles along the processes of DRG neurons cultured from TgGFP-dynamitin mice. A corresponding line scan of relative fluorescent intensity along the neurite emphasizes the punctate nature of the localization. (B) MT motor proteins cytoplasmic dynein (DHC and DIC), kinesin-1 (KHC), and kinesin-2, and dynactin (p50), axonal transport markers synaptotagmin and synaptophysin, and late endosome markers LAMP-1 and Rab-7 co-purify with isolated vesicles. GFP-labeled dynamitin is efficiently incorporated into the vesicle-associated dynactin complex. Fractions from the vesicle purification include initial cytosolic (S) and membrane (P) fractions from mouse brain homogenate and the 0.6 M (0.6), the 0.6/1.5 M (V), and 1.5 M and 2.5 M (1.5 and 2.5) steps from a discontinuous sucrose gradient. (C) Vesicles isolated from the 0.6/1.5 M interface were incubated with MTs and analyzed by negative stain EM (left panel). Vesicles had a mean diameter of 90.0 ± 2. 9 nm (SE, n=311). (D) Stepwise quantitative photobleaching of dispersed vesicles produced a bimodal distribution. For comparison, photobleaching data for soluble purified dynein/dynactin [2] is shown (red bars). (E) Quantitative western blotting was performed to measure vesicle-bound cytoplasmic dynein, dynactin, kinesin-1 and kinesin-2.