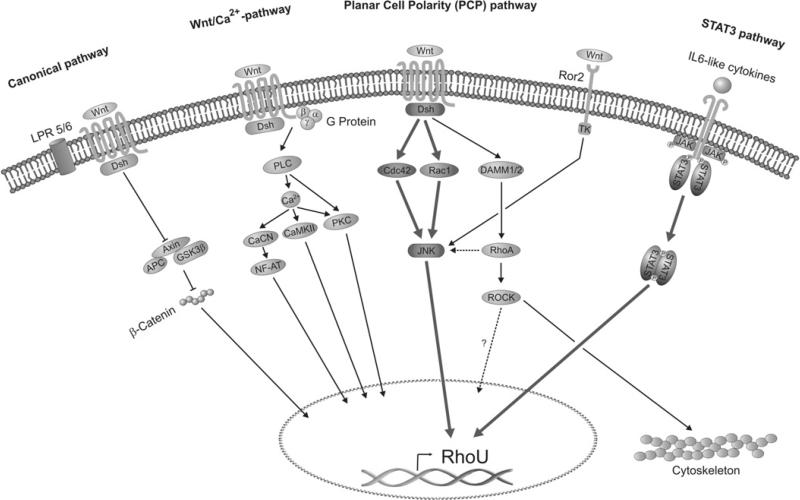
Figure 7. Schematic representation of the best known Wnt signal transduction pathways.
The Wnt signal branches into three main pathways: the canonical β-catenin-dependent, the non-canonical planar cell polarity (PCP) and Wnt-Ca2+. All of these pathways are thought to occur through the Frizzled receptor and Dishevelled. Other receptors have recently been shown to be able to activate additional non-canonical pathways. In particular the Ror2 receptor, depicted here, converges on to JNK in a similar manner to the Wnt/PCP pathway. In the present study we have demonstrated that RhoU is transcriptionally induced both by Wnt-1, through the PCP pathway involving the Rho GTPases Rac1/Cdc42 and the MAPK JNK, and by gp130 cytokines through the JAK/STAT3 pathway (thick lines). APC, adaptor protein complex; CaCN, calcineurin; CaMKII, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; Dsh, Dishevelled; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; LPR 5/6, lipoprotein receptor 5/6; NF-AT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; PLC, phospholipase C; TK, tyrosine kinase.