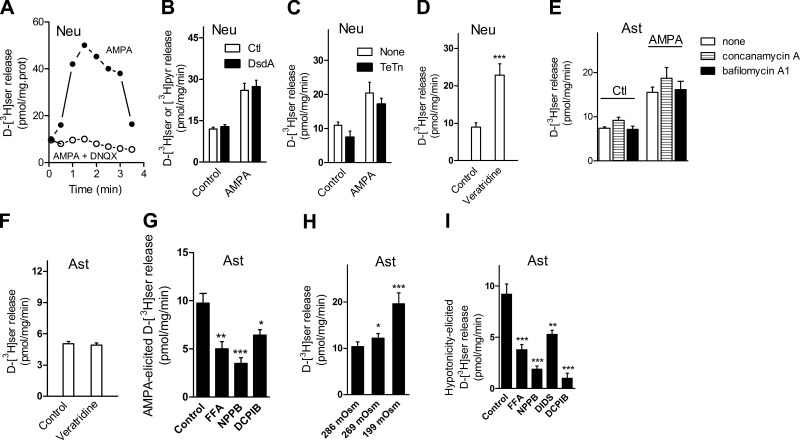
Figure 2.
Characteristics of d-[3H]serine release from primary cultures of neurons and astrocytes. A) d-[3H]serine release elicited by 100 μM AMPA and 50 μM cyclothiazide (solid circles) from neuronal cultures was blocked by 5 min preincubation with 20 μM DNQX (open circles). B) Addition of 10 μg/ml DsdA in release medium supplemented with 4 mM unlabeled pyruvate did not change the release elicited by 100 μM AMPA and 50 μM cyclothiazide. C) A 24-h preincubation with 2 μg/ml tetanus toxin (TeTn) failed to significantly inhibit AMPA/cyclothiazide-elicited d-[3H]serine release from neuronal cultures. D) Stimulation of d-[3H]serine release from neuronal cultures by 50 μM veratridine. E) A 1-h preincubation with 1 μM bafilomycin A1 or 1 μM concanamycin A had no effect on AMPA/cyclothiazide-elicited d-[3H]serine release from primary astrocyte cultures. F) Lack of effect of 50 μM veratridine on d-[3H]serine release from primary astrocyte cultures. G) Inhibition of AMPA/cyclothiazide-elicited d-[3H]serine release from primary astrocyte cultures by the VRAC blockers FFA (100 μM), NPPB (100 μM), and DCPIB (20 μM). H) Exposure to hypotonic medium increases rate of d-[3H]serine release from primary astrocyte cultures. I) inhibition of the hypotonicity-mediated d-[3H]serine release by FFA (100 μM), NPPB (100 μM), DIDS (100 μM), or DCPIB (20 μM) in primary astrocyte cultures. Hypotonicity-mediated release was calculated by subtracting release of d-serine observed in 286 mosmol from that in 199 mosmol in the absence and in the presence of drugs. Results are representative of 3 different experiments with different cultures (A) or represent average ± se of 4–9 experiments with different cultures done in quadruplicates (B–I). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control. Neu, neurons; Ast, astrocytes.