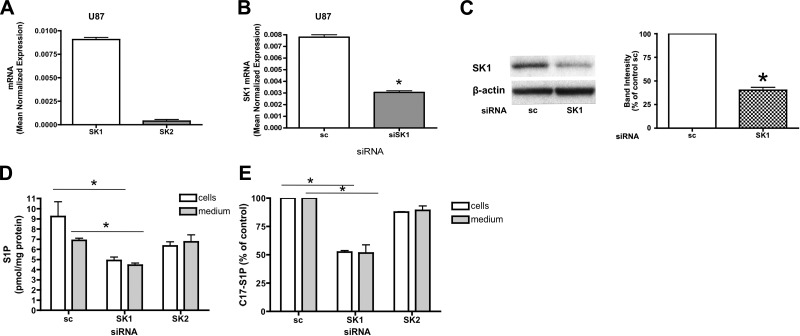
Figure 4.
SK1 down-regulation causes intra- and extracellular decrease of S1P in U87MG cells. A) U87MG cells were subjected to mRNA extraction and real-time PCR analysis for hSK1 and hSK2. Real-time PCR data are expressed as mean ± sd normalized expression of 3 independent experiments, using β-actin as a reference gene. B) U87MG cells treated with 20 nM scrambled (sc) or SK1 siRNA for 72 h were collected using PARIS kit lysis buffer and subjected to mRNA extraction and real-time PCR analysis for hSK1. Real-time PCR data are expressed as mean ± sd normalized expression of 3 independent mRNA extractions, using β-actin as a reference gene. C) Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot. Membranes were probed with the following antibodies: hSK1 (1:500) and actin (1:10,000). Blot is representative of 3 separate experiments performed in duplicate. D) U87MG cells treated with sc or SK1 siRNA for 72 h were incubated for 2 h in trapping medium (described in Materials and Methods). At the end of incubation, cells were collected and analyzed by mass spectrometry for intracellular and extracellular S1P content. Results are means ± sd (pmol/mg protein) of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. E) U87MG cells treated with sc or SK1 siRNA as described above were incubated for 2 h in trapping medium and pulsed for 10 min with C17-d-erythro-sphingosine to a final concentration of 1 μM. C17-S1P was measured in the cells and in the medium by mass spectrometry. Results are mean ± sd percentage compared to control of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *P < 0.05.