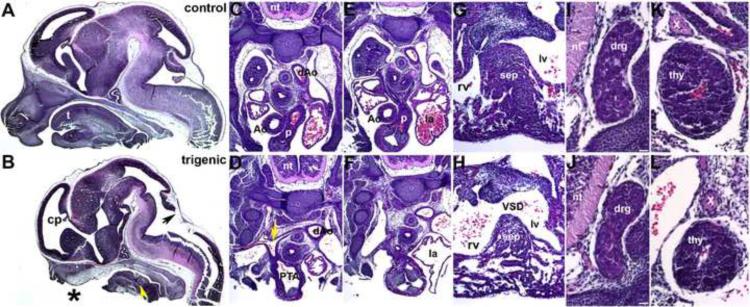
Figure 3. Histological examination of E13.5 Smad7 trigenic phenotypes fed doxycycline at E7.5.
(A,B) Control and trigenic littermate cranial regions sectioned sagittally and stained with H&E. Note the absent ventral extremity of the lower jaw and lip, hypoplastic tongue, absent primary palate, and absent upper jaw and lip in trigenic mutant (* in B). However, Meckel's cartilage is still present in the mutant (yellow arrowhead). Whilst the choroid plexus (cp) extending into the trigenic lateral ventricle is present, the choroid plexus differentiating from the roof of the fourth ventricle is absent (arrow in B). (C–H) Low power images of serial sagittal sections through control (C,E,G) and trigenic (D,F,H) cardiothoracic regions at the level of the OFT and high power images of the interventricular septum (G,H). While the control has separate ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk vessels (C,E), the trigenic mutant outflow tract has failed to septate and remains as a single outlet (PTA; E) and the right subclavian is retroesophageally located in the trigenic embryo (arrow in D). Additionally, the trigenic embryo exhibits accompanying interventricular septal defects (H). (I–L) Higher power images of transverse sections reveal that both the trigenic dorsal root ganglia (J) and thymus (L) are histologically normal when compared to control littermates (I,K), but are proportionately smaller in line with the overall reduced size of the trigenics. Abbreviations: t, tounge; nt, neural tube; PTA, Persistent Truncus Arteriosus; VSD, Ventricular Septum Defect; sep, septum; rv, right ventricle; lv, left ventricle; la, left ventricle; Ao, aortic trunk; dAo, descending aorta; p, pulmonary trunk; drg, dorsal root ganglia; thy, thymus; X, vagal X trunk. Bars in I,J=10μm.