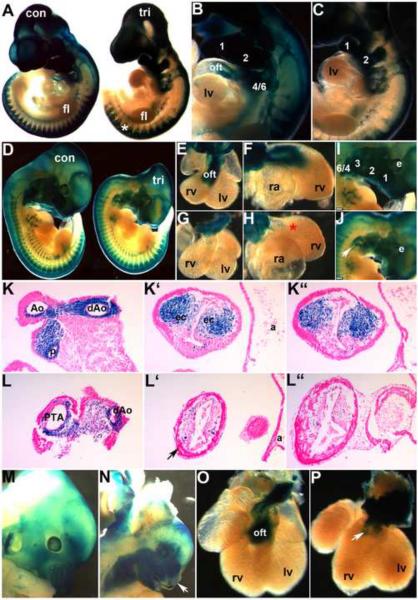
Figure 4. NCC develop in Smad7 trigenic mutant embryos fed doxycycline at E7.5.
To lineage map both the trigenic and control NCC populations, R26r lacZ reporter mice were crossed with Smad7 trigenic to enable us to visualize NCC migration and colonization of the craniofacial and OFT regions. (A–C) E10 wholemount lacZ staining of trigenic and control littermates, revealed that initial NCC migration was largely unaffected within the trigenic (right embryo in A) cranial, cardiac and trunk regions when compared to control littermates. Robust lacZ expression is evident in trigenic frontonasal prominence, trigeminal nerve ganglia, hypoplastic 1st, 2nd and 3rd arches and within the facial nerve ganglia, and primordium of the 3rd pharyngeal arch. Similarly, lacZ-marked NCC are present within the cardiac 4/6th arch region and the DRGs (*) in trigenic mutants. (D–J) LacZ stained E11.5 trigenic and control littermate whole embryos (D); isolated control (E,F) and trigenic (G,H) hearts viewed frontally (E,G) and from the right (F,H); and higher power views of control (I) and trigenic (J) craniofacial regions. Note there is a deficiency of NCC-derived Schwann cells within SNS of trigenic forelimb (* in D), but trunk NCC migration is unaltered. (E–H) Higher power views of isolated hearts clearly show that Smad7 trigenic NCC reach the pharyngeal arches and aortic sac region, that a few mutant NCC can enter the OFT truncal region but that there are no lacZ stained NCC within the trigenic OFT conal region (* in H) when compared to controls (E,F). Similarly, although trigenic NCC do colonize the hypoplastic craniofacial regions, there are reduced numbers of lacZ positive cells, particularly evident within the frontal nasal process and 3rd, 4th and 6th pharyngeal arches (arrow in J). (K,L) Sections through OFT from distal to proximal in E11.5 control (K, K', K”) and trigenic embryos (L, L', L”). Histology confirms a lack of trigenic NCC colonizing the OFT, that there are fewer cells within the conal cushions and that the mutant NCC are not found in ectopic locations within the adjacent myocardial cuff (arrow in L') or overlying endothelium. (M–P) LacZ stained E13.5 control (M,O) and trigenic littermate whole embryos and isolated hearts viewed frontally. Note the absent lacZ NCC within the trigenic upper and lower craniofacial regions (arrow in N) and the absence of lacZ positive NCC within the trigenic OFT (arrow in P). Abbreviations: fl, forelimb; lv, left ventricle; a, atria; oft, outflow tract; ec, endocardial cushions; rv, right ventricle; ra, right atria; e, eye. Bars in I,J=0.2mm.