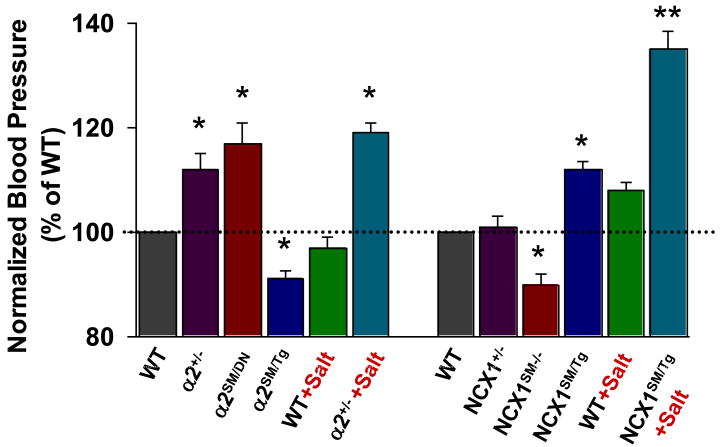
Fig. 4.
Relative blood pressures of mice with genetically-engineered α2 Na+ pumps and NCX1. The data from several sources, are normalized to the BPs of the respective control wild type (WT) mice. Mice with a null mutation in one α2 Na+ pump allele (α2+/-) [36] or smooth muscle-specific α2 knockdown (α2SM/DN) (Song, Chen, Zhang, Lee, Kotlikoff and Blaustein, unpublished), or increased smooth muscle-specific NCX1 overexpression (NCX1SM/Tg) [166], had significantly elevated BP. A high salt diet augmented the elevated BP in α2+/- mice (4% NaCl × 2 weeks) and NCX1SM/Tg mice (8% NaCl + 1% NaCl in tap water × 4 weeks). Smooth muscle-specific overexpression of α2 Na+ pumps (α2SM/Tg)[187] or knockdown of NCX1 (NCX1SM-/-) [198] significantly reduced BP. * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01 vs WT or the respective genotypes on a normal (0.5%) salt diet. Reprinted with permission [65].