Figure 2. The relationships between pluripotency, cell cycle and cell size control.
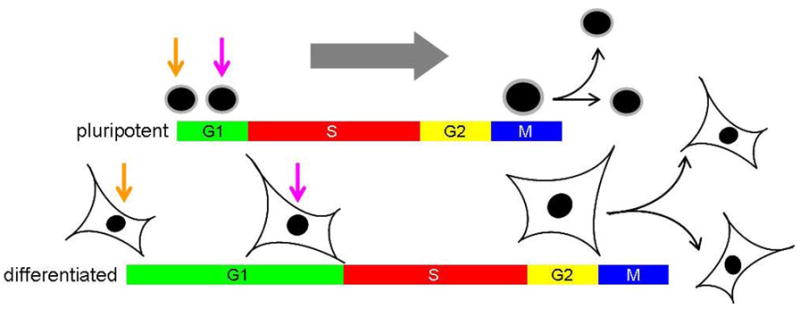
The figure represents a summary of the pathways discussed throughout this review, now thought to be important for cell cycle and cell size control in pluripotent cells. The core transcriptional network inherent to pluripotent stem cells impacts on this network at several points. Evidence links Myc to all major points in the regulatory network. For example, Myc regulates the cell cycle directly through regulation of Cdk activity and indirectly through miRNAs. We speculate that accelerated progress through G1 can account for the small size of pluripoent cells. Interestingly, cells with inactive Rb-family members progress through G1 rapidly and have reduced cell volume.
