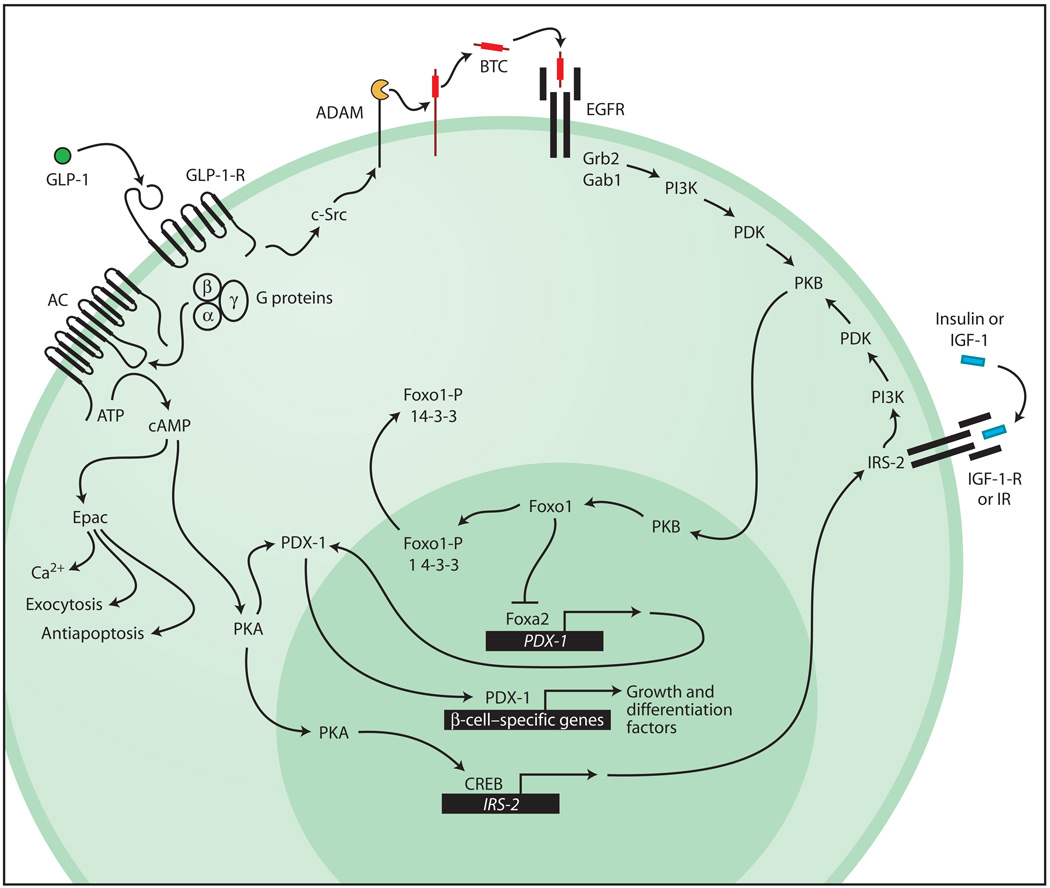
Fig. 1.
GLP-1 acts by means of the GLP-1-R to stimulate adenylyl cyclase (AC), and thereby cAMP production, and to activate the cAMP-binding proteins PKA and Epac. PKA promotes translocation of PDX-1 to the nucleus, where it binds to regulatory elements within the enhancer or promoter sequences of genes important to β-cell growth and differentiation (13, 32). PKA also acts by means of CREB to up-regulate expression of IRS-2. Actions of Epac include a stimulation of intracellular Ca2+ signaling (5), secretory granule exocytosis (5), and the promotion of β-cell survival (33). Binding of GLP-1 to the GLP-1-R transactivates the EGFR in a manner mediated by c-Src and the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase)–family metalloproteinase. Liberation of the soluble EGFR ligand betacellulin (BTC) stimulates EGFR autophosphorylation and promotes formation of an EGFR-Grb2-Gab1-PI3K complex with resultant activation of PKB. The IR and IGF-1-R signaling pathways acting by means of IRS-2 and PI3K converge with the GLP-1-R signaling pathway at PKB. Activated PKB translocates to the nucleus, where it acts at Foxo1 to disinhibit Foxa2-dependent PDX-1 gene promoter activity. Phosphorylated Foxo1 (Foxo1-P) associates with 14-3-3 proteins and is exported out of the nucleus to accumulate in the cytosol.