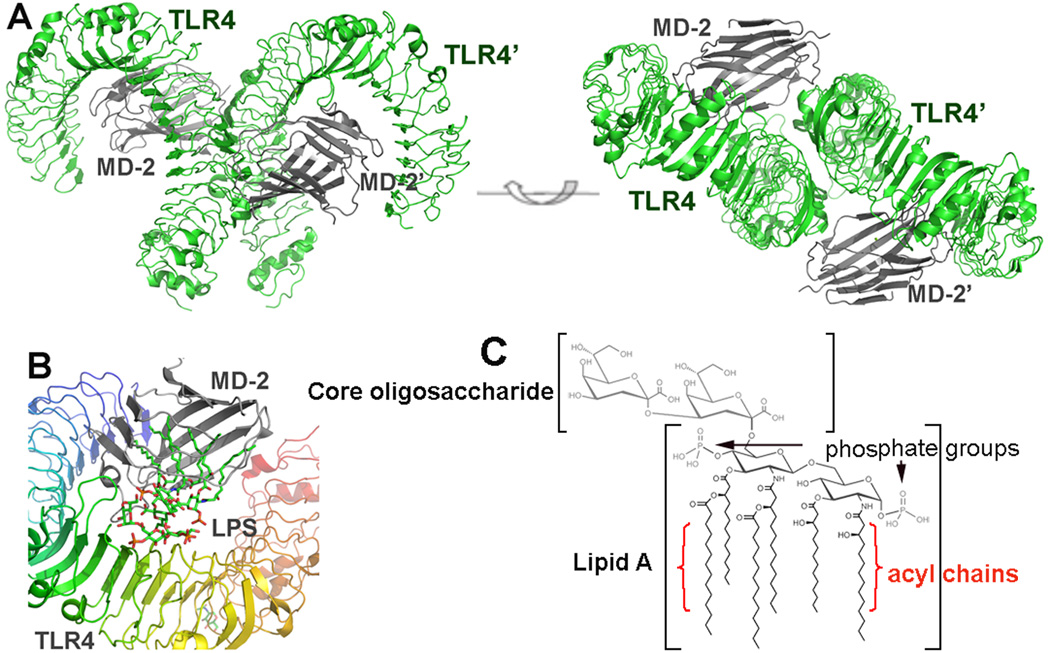
Figure 2.
Overall structure of the TLR4/MD-2 complex. (A) Side and top view of an m-shaped receptor multimer composed of two copies of the TLR4/MD-2 complex arranged symmetrically. (B) Close-up view of the LPS binding site on the TLR4/MD-2 interface. LPS interacts with a large hydrophobic pocket in MD-2 and directly bridges the two components of the multimer. The primary interface between TLR4 and MD-2 is formed before binding LPS, and the dimerization interface is induced upon LPS binding. (C) Molecular structure of LPS.