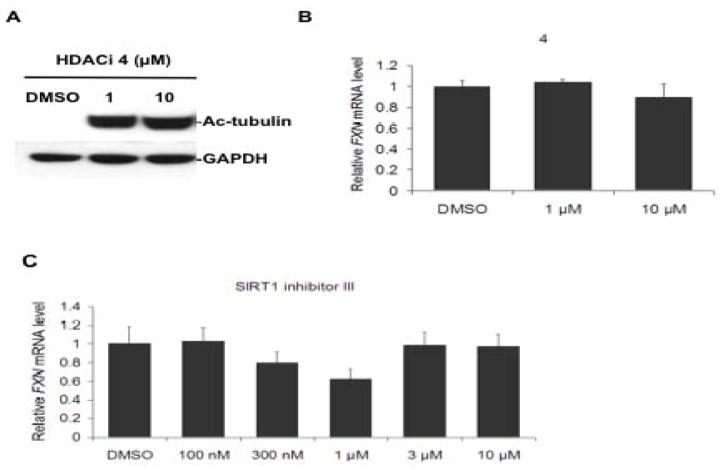
Figure 6.
A class II HDAC inhibitor and a Sirt1 inhibitor fail to activate FXN gene expression. (a) Class II HDAC inhibitor 4 causes tubulin acetylation in FRDA cells. FRDA lymphoblasts were incubated with the indicated concentrations of 4 or DMSO alone (at 0.1%) for 24 h in culture medium, prior to SDS-PAGE and western blotting with anti-ac-tubulin antibody, or antibody to GAPDH, as a loading control. (b) HDAC inhibitor 4 fails to activate FXN gene expression. FRDA lymphoblasts were incubated in culture media containing either 0.1% DMSO, as a control, or 4, at the indicated concentrations in 0.1% DMSO, for 24 h prior to determination of FXN mRNA levels by qRT-PCR, using GAPDH mRNA as an internal control. The y-axis denotes FXN mRNA levels, normalized to GAPDH mRNA, relative to the DMSO control, set to 100%. Each determination was done in triplicate, and the SEM is shown. (c) The Sirt1 inhibitor 6-chloro-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-1-carboxamide fails to up-regulate FXN gene expression in primary lymphocytes from a FRDA patient. Lymphocytes were incubated in culture media containing either 0.4% DMSO, as a control, or with the indicated concentrations of inhibitor in 0.4% DMSO, for 48 h prior to determination of mRNA levels by qRT-PCR, using GAPDH as an internal control, as in panel b.