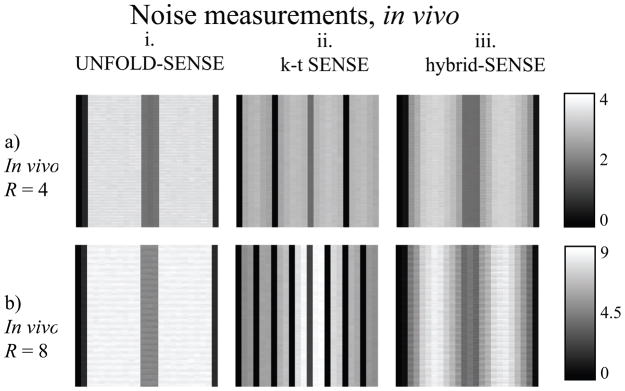
Figure 9.
Noise amplification maps, for the in-vivo data, were evaluated using the Monte Carlo approach. Lower acceleration settings at or near DC are associated with smaller noise amplification. The k-t SENSE regularization scheme allowed good noise suppression at high temporal frequencies (a.ii and b.ii), while UNFOLD-SENSE with ZTR performed well at low temporal frequencies (a.i and b.i). The performance of hybrid-SENSE (a.iii and b.iii), not surprisingly, is a compromise between the two other methods.