Figure 1.
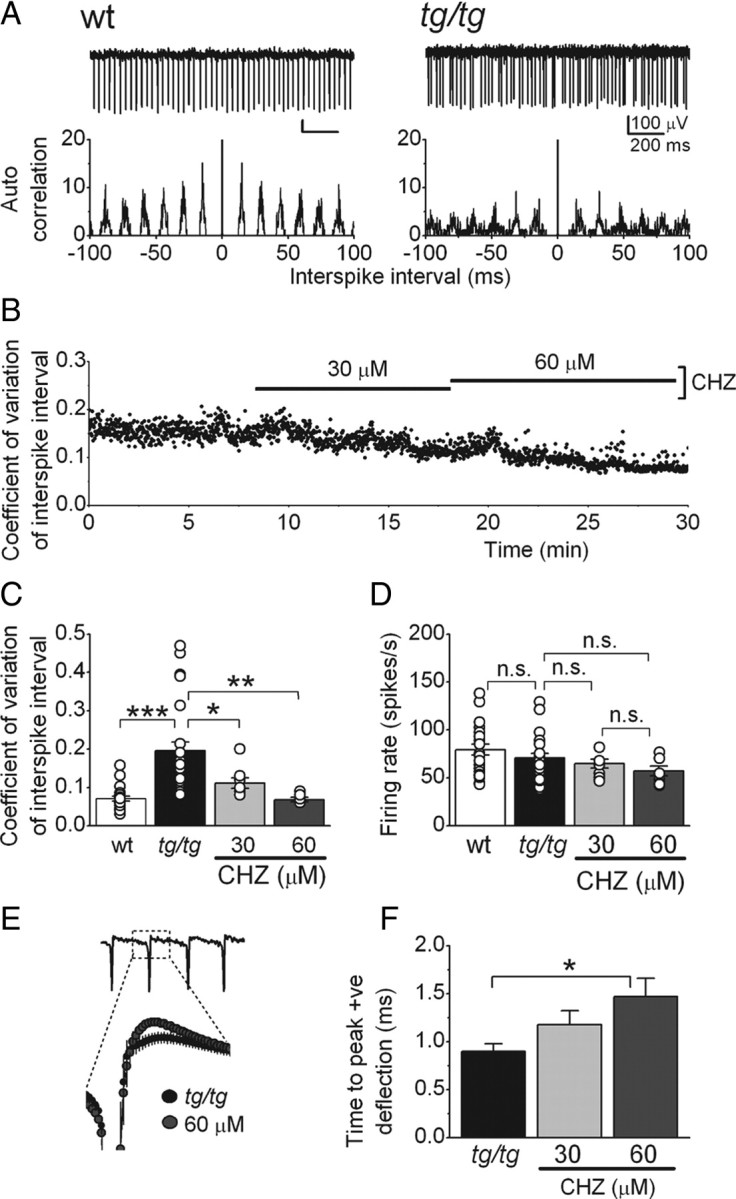
CHZ decreases the irregularity of the intrinsic pacemaking of tg/tg Purkinje cells. A, Raw traces from extracellular recordings from wild-type (+/+; wt) and tg/tg Purkinje cells, with their interspike interval autocorrelograms below. Note the irregular firing of the tg/tg cell. B, CHZ dose dependently decreased the variation of the interspike interval in a tg/tg Purkinje cell whose spontaneous activity was extracellularly recorded. C, Average and individual values (circles) of the coefficient of variation of the interspike intervals in +/+ and tg/tg Purkinje cells. Note the higher values and the wider distribution of coefficient of variation in the mutant cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni's correction); n = 24 cells for tg/tg mice and n = 19 cells for +/+ mice. D, Average and individual (circles) firing rates of the +/+ and tg/tg Purkinje cells shown in C. n.s., Not significant. E, CHZ increased the magnitude of the positive deflection of the spikes recorded extracellularly in tg/tg Purkinje cells. The expanded figure shows an averaged trace of the activity of seven cells, in control and after adding CHZ at 60 μm. F, Average magnitude of the positive deflection in control and after adding CHZ in increasing concentrations. *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni's correction).
