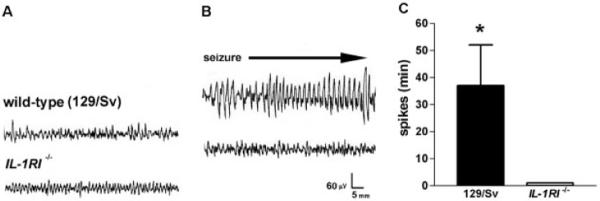
Fig 3.
High doses of interleukin (IL)-1β (116ng) result in limbic behavioral and electrical seizures only in wild-type mice. (A, B) Hippocampal electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings from mice before (A) and 3 hours after IL-1β administration (B). (A) Normal EEGs in wild-type (129/Sv) and IL-1R1−/− mice. (B) Differential effects of IL-1β in these two groups include: prolonged spike trains develop in wild-type 129/Sv mice, whereas the EEG remains normal in IL-1R1−/− mice. (C) Quantitative analysis of IL-1β–induced spike duration in the 6 hours after administration. IL-1β induces limbic seizures, with a mean duration of 37.0 ± 15.2 minutes (n = 5), in all wild-type mice, whereas no IL-1R1−/− mice (n = 5) experienced development of seizures.