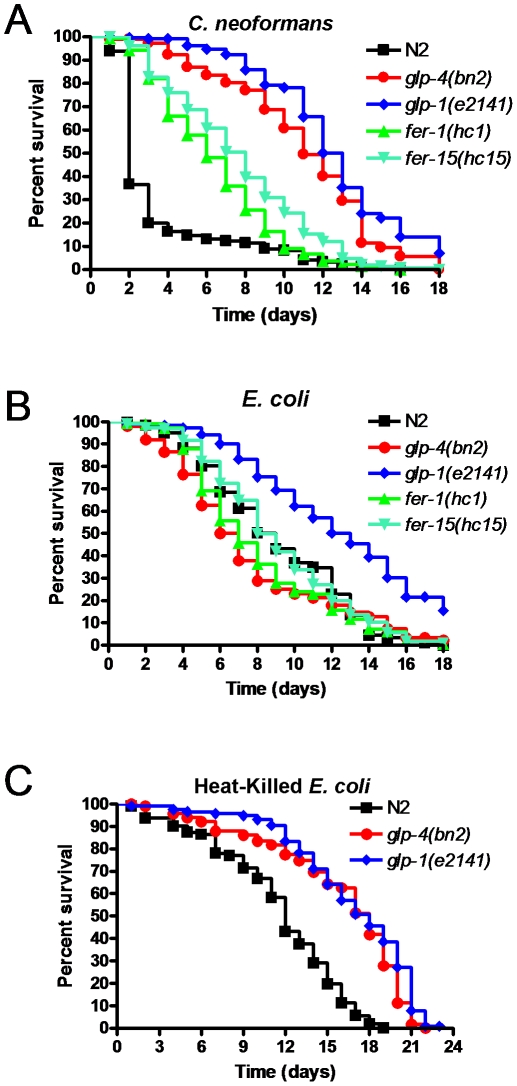
Figure 2. The increased resistance germline-deficient mutants glp-1 and glp-4 is independent of effects on matricide.
(A) Wild-type, glp-4(bn2) mutant, glp-1(e2141) mutant, fer-1(hc1) mutant, and fer-15(hc15) mutant nematodes were exposed to C. neoformans. When compared to wild-type nematodes, all four mutants showed significant differences (P<0.0001). Significant differences were also found when glp-4(bn2) mutants or glp-1(e2141) mutants were compared to fer-1(hc1) (P<0.0001; P<0.0001 respectively) or to fer-15(hc15) (P<0.0001; P<0.0001 respectively) mutants. (B) Wild-type, glp-4(bn2) mutant, glp-1(e2141) mutant, fer-1(hc1) mutant, and fer-15(hc15) mutant nematodes were exposed to E. coli. When compared to wild-type nematodes, only glp-1(e2141) mutants showed significant increases in resistance (P<0.0001). (C) Wild-type, glp-4(bn2) mutant, and glp-1(e2141) mutant nematodes were placed on lawns of heat-killed E. coli and survival was measured. When compared to wild-type nematodes, both glp-4(bn2) mutants (P<0.0001) and glp-1(e2141) mutants (P<0.0001) showed significant differences. 120–300 nematodes were used in each condition.