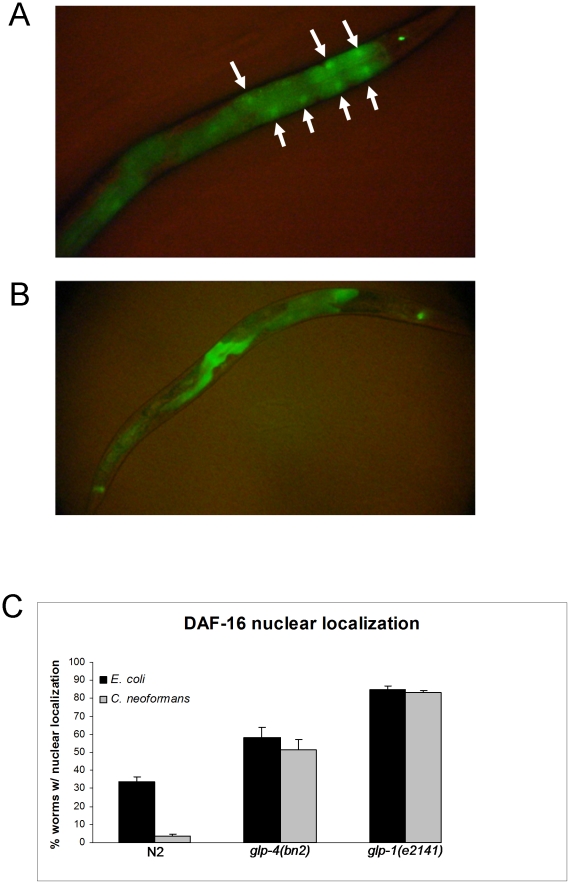
Figure 4. The germline-deficient mutants glp-1 and glp-4 have higher levels of DAF-16 activation than wild-type animals regardless of pathogen exposure.
(A) A glp-1(e2141) mutant nematode expressing a daf-16:gfp transgene under control of Pgly-19 after exposure to E. coli. (B) A wild-type nematode expressing a daf-16:gfp transgene under control of Pgly-19 after exposure to E. coli. (C) Wild-type, glp-4(bn2) mutant, and glp-1(e2141) nematodes expressing transgenic DAF-16:GFP under control of Pgly-19 were exposed to either E. coli or C. neoformans and categorized as predominately nuclear or cytoplasmic as described in Section 3.4.8. Significant differences were found when glp-4(bn2) mutants were compared to wild-type on both E. coli (P = 0.0003) and C.neoformans (P<0.0001). Likewise, significant differences were also found when glp-1(e2141) mutants were compared to wild-type on both E. coli (P<0.0001) and C. neoformans (P<0.0001). No significant differences were found when comparing the two glp-4(bn2) groups (P = 0.4363) nor with the two glp-1(e2141) groups (P = 0.7802), but there were significant differences in DAF-16 localization between the wild-type nematodes on E. coli and C. neoformans (P = 0.0002).