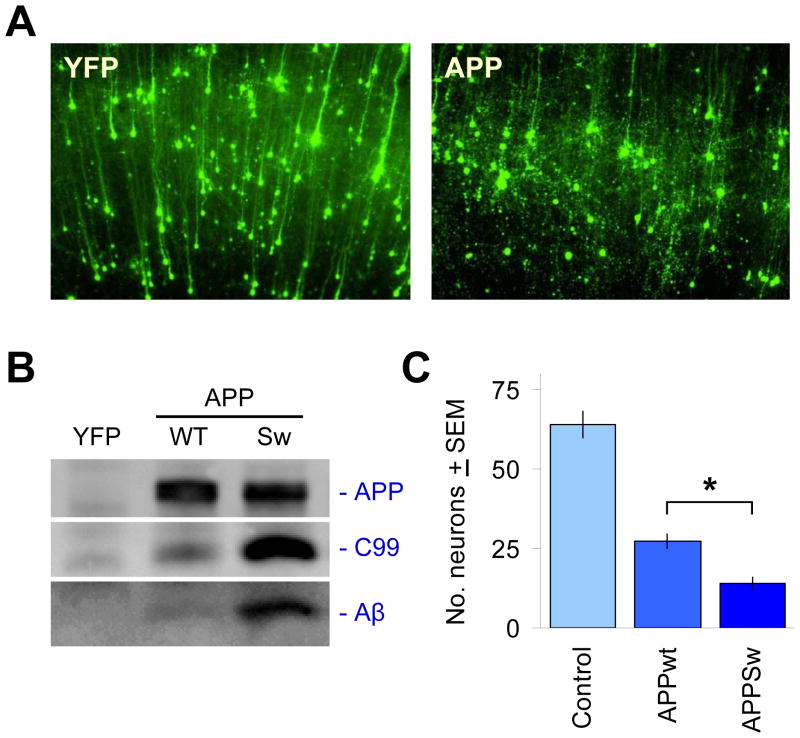
Figure 3. Acute challenge with APP isoforms leads to its proteolytic processing into Aβ and the induction of neuronal degeneration.
(A) The co-transfected YFP fluorescent marker clearly delineates neuronal cell bodies and dendrites after 2–3 d in culture, shown in the left panel for a region in cortex (pia surface up). It can be seen that the majority of neurons transfected are cortical pyramidal neurons, easily distinguished by their extension of a single, prominent apical dendrite in the radial direction. Right panel shows overt neurodegeneration of such cortical pyramidal neurons 2–3 days after co-transfection with APP isoforms such as APPSw. (B) Expression of APP is readily detected in transfected brain slices via immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the human-specific APP antibody 6E10. Processing of APP into C99 and Aβ by native tissue proteases can also be seen, with higher levels of C99 and Aβ production as expected for APPSw relative to APPWT. (C) Induction of neurodegeneration by transfected APP is more severe with the Swedish mutation. Ordinate axis shows average, total numbers ± SEM of non-degenerating pyramidal neurons in the cortical regions of each explant, N=12 brain slices scored per condition. *, significant by ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc comparison test at the 0.05 confidence level.