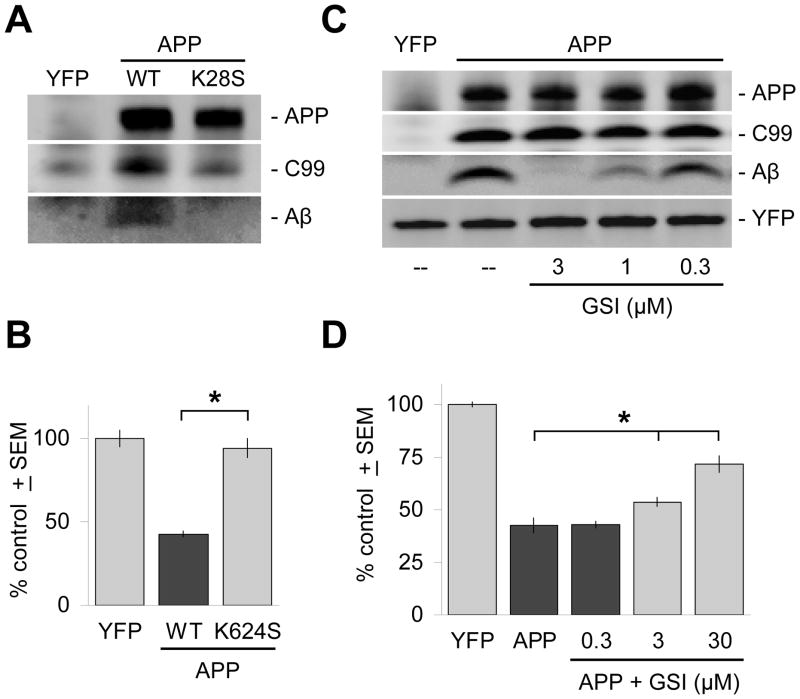
Figure 4. Inhibition of γ-secretase cleavage inhibits Aβ production and is neuroprotective.
(A) The APPK624S mutation inhibits γ-secretase cleavage of APP and decreases Aβ production to undetectable levels in 6E10 immunoblots of brain slice lysates, but does not significantly affect levels of expression of full-length APP. (B) Correspondingly, transfection with the APPK624S mutation does not result in measurable levels of neurodegeneration. (C) Treatment of transfected brain slices with the γ-secretase inhibitor WYGSI-04 (“GSI”) for 2 days resulted in selective, dose-dependent inhibition of Aβ production. Such immunoblot analysis showed that WYGSI-04 treatment had no effect on the expression of full-length APP, or on its initial cleavage by endogenous β-secretases to the intermediate fragment C99. Lanes were loaded with identical amounts of total protein from brain slice lysates, with equivalent transfection rates confirmed by direct immunoblotting against the co-transfected marker YFP (bottom band). “--” denotes treatment with the DMSO vehicle only. (D) Correspondingly, inhibition of Aβ production by WYGSI-04 provides dose-dependent neuroprotection in the same concentration range. Ordinate axes in (B) and (D) show average, total numbers ± SEM of non-degenerating pyramidal neurons in the cortical regions of each explant expressed as a percentage of control brain slices transfected with YFP only. *, significant by ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc comparison test at the 0.05 confidence level.