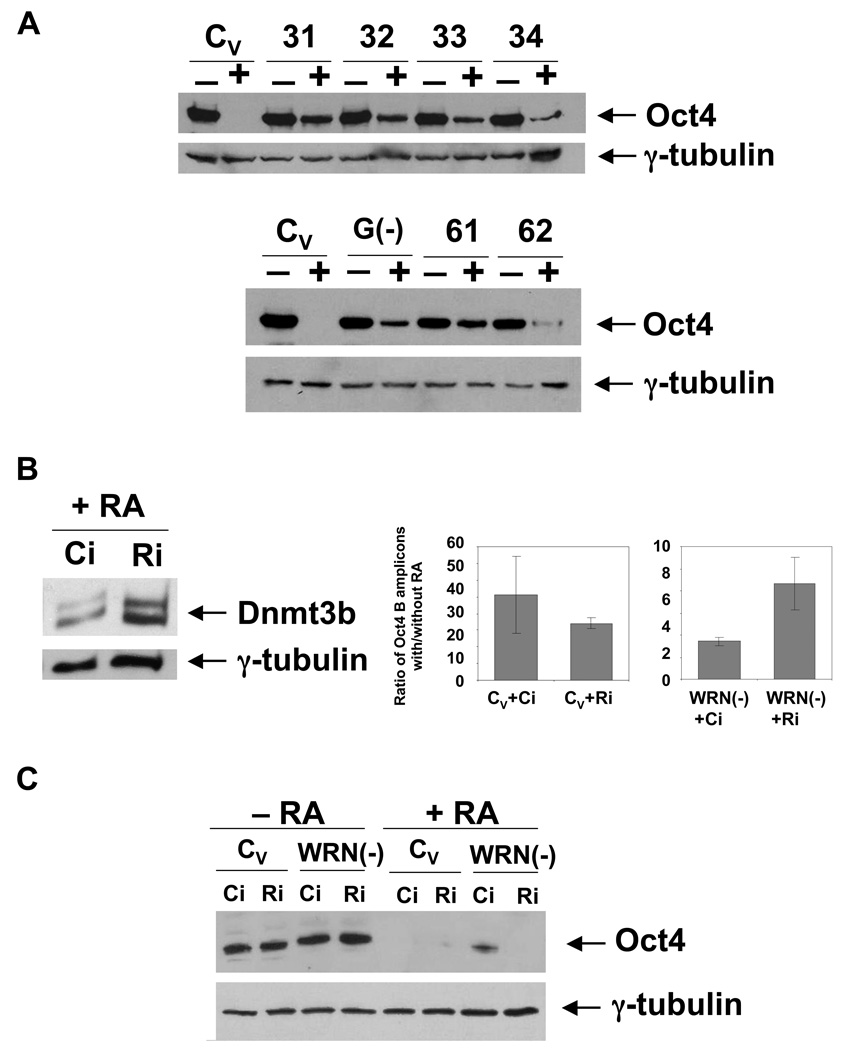
Fig. 7. Oct4 expression and Oct4 promoter methylation status in RA-treated WRNp-deficient cells.
(A) RA-treated WRNp-deficient cells continue to express Oct4. WRNp-deficient (31–62), G9a-deficient [G(−)] and control (CV) cells were treated with 10 µM RA for 7 days, after which cells were harvested and Oct4 expression analyzed by western blotting (+, cells treated with RA; −, untreated, control samples). (B) Rbl2 knockdown stimulates Dnmt3b expression and reverses the Oct4 promoter methylation defect of WRNp-deficient cells. The day following RA addition, cells were treated with siRNA targeting Rbl2. Left – Dnmt3b expression in WRNp-deficient cells (61) treated with control (Ci) or Rbl2 siRNA (Ri) at 5 days after RA addition. Right – DNA methylation in the Oct4 promoter B region. (C) Oct4 expression in differentiated (+RA) and undifferentiated (−RA) control and WRNp-deficient cells treated with siRNA. Cells were treated as in B. Oct4 expression was analyzed by western blotting 7 days after RA addition.