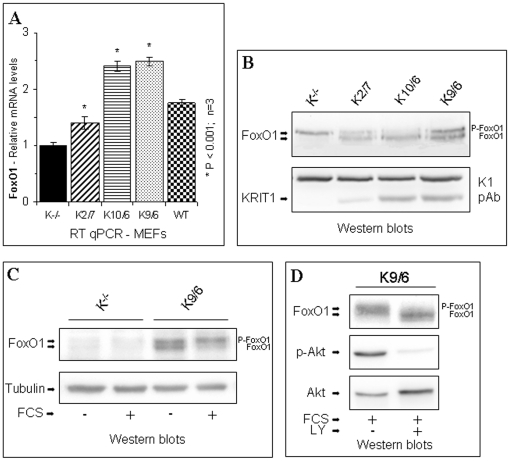
Figure 5. KRIT1 regulates FoxO1 expression and activity.
Wild-type (WT), KRIT1−/− MEFs (K−/−) and Lv-KRIT1 MEFs re-expressing KRIT1 at low, medium and high levels, respectively (K2/7, K10/6 and K9/6), were analyzed by RT-qPCR and Western blot as described in Materials and Methods. A) RT-qPCR analysis of FoxO1 mRNA expression levels. Results are expressed as relative mRNA level units referred to the average value obtained for the KRIT1−/− (K−/−) samples, and represent the mean (± SD) of n≥3 independent RT-qPCR experiments. *P<0.001 versus KRIT1−/− cells. Notice that KRIT1 re-expression in KRIT1−/− cells caused a significant, dose-dependent upregulation of FoxO1 mRNA levels. B–D) Western blot analysis of FoxO1 protein expression in confluent KRIT1−/− and Lv-KRIT1 MEFs. Cells were grown to confluence in standard culture conditions, and lysed (B). Alternatively, confluent cells were serum-starved overnight (C) and either left untreated (-FCS) or treated with 10% FCS for 15 min (+FCS) before lysis. In the FoxO1 blots, the upper and lower bands are the phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of FoxO1, respectively. (D) To demonstrate that the upward electrophoretic mobility shift of FoxO1 was Akt-dependent, confluent cells were serum-starved overnight and treated with 10% FCS for 15 min (+FCS) either in the absence (-LY) or in the presence (+LY) of the PI3K/Akt pathway inhibitor LY294002. Phospho-Akt levels were determined with an antibody to phospho-serine 473. The undetermined 95 kDa band detected by the K1 antibody and Tubulin served as loading controls. Notice that the expression level of FoxO1 is reduced and the ratio of phosphorylated to unphosphorylated forms of FoxO1 is increased in KRIT1−/− MEFs compared with Lv-KRIT1 MEFs.