Figure 1.
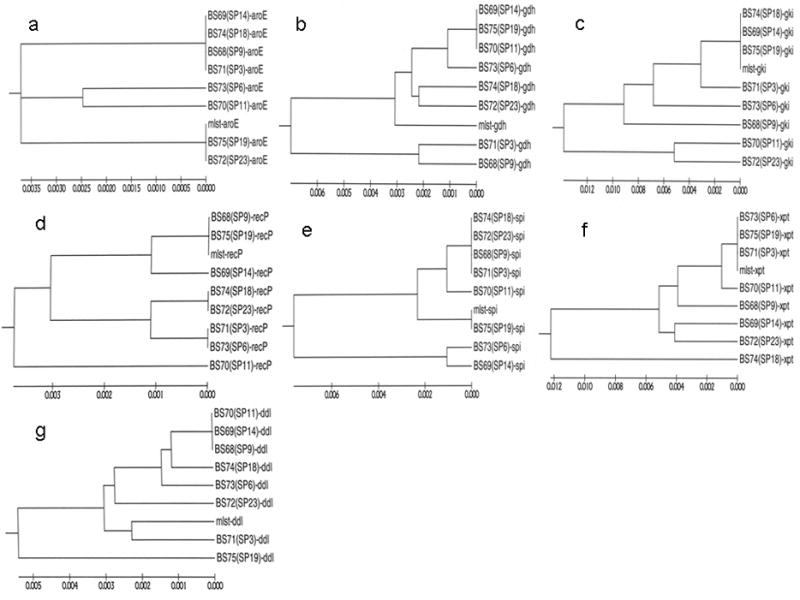
Phylogenetic trees were built for each of seven S. pneumoniae core genes using the same set of eight clinical strains. Each gene produces a different tree stucture (from the same set of strains) demonstrating the mosaic nature of the S. pneumoniae genome in general which results from extensive and continuous horizontal gene transfer. (a) – (g): Phylogenetic trees showing the relative distances of seven housekeeping loci among the eight clinical strains of S. pneumoniae including: a) the aroE gene encoding shikimate dehydrogenase; b) the gdh gene encoding glutamate dehydrogenase; c) the gki gene encoding glucose kinase; d) the recP gene encoding the RecP recombination protein; e) the spi gene encoding a signal peptidase; f) the xpt gene encoding xanthine phosphoribosyltransferase; and g) the ddl gene encoding D-alanyl-D-alanine ligase. Reference sequences were downloaded from http://www.mlst.net.mlst-aroE, mlst-gdh, mlst-recP, mlst-spi, mlst-xpt and mlst-ddl; h) Phylogenic tree reconstructed using concatenated sequences from all seven house-keeping genes (3,199 bp) of S. pneumoniae. Concatenated sequence mlst-7gene was made by using seven reference gene sequences from http://www.mlst.net.
