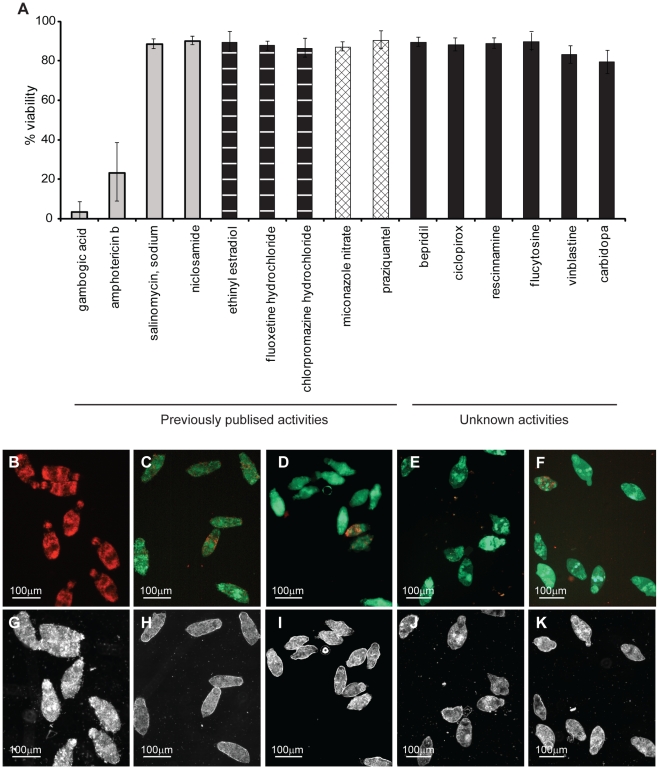
Figure 6. Application of the dual-fluorescent viability assay for determining the anti-schistosomula effect of selected compounds with previously-described or unknown activities.
Mechanically-transformed schistosomula were cultured for 24 hr, incubated with compounds (10 µM) for an additional 24 hr, washed and subsequently co-stained with both PI and FDA. PI- (544 nm, collected at 20 min) and FDA- (485 nm, collected at 5 min) fluorescence intensity units were converted into viability measures according to the formula described in the Methods . (A) Calculated schistosomula viability in response to each compound tested (further details can be found in Dataset S1). Representative epi-fluorescent and plane polarized microscope images of schistosomula treated with (B and G) gambogic acid, (C and H) sodium salinomycin, (D and I) niclosamide, (E and J) praziquantel and (F and K) ciclopirox are indicated. Compounds designated as having ‘previously published activities’ (grey histograms – death, vertical lines within histograms – overactive, hatched lines within histograms – rounded) were selected from those described by Abdulla et al. [10] while those compounds indicated as having ‘unknown activities’ (black histograms) were selected from Berriman et al. [3]. These results are representative of two independent experiments.