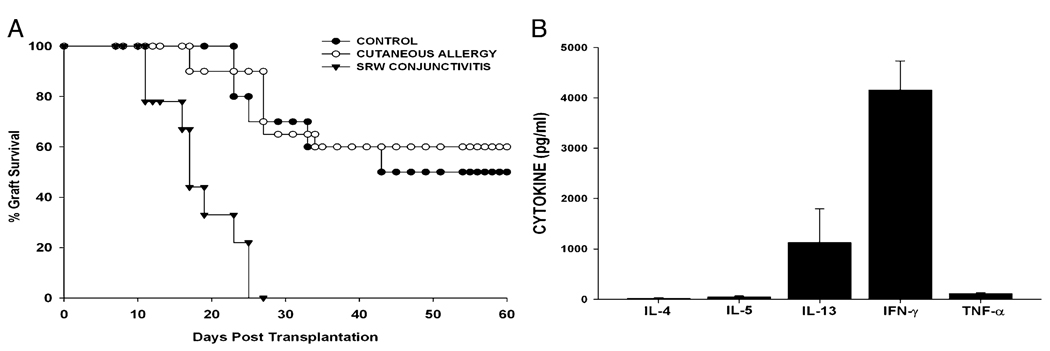
FIGURE 4.
Effect of cutaneous immediate hypersensitivity on corneal allograft rejection and cytokine production by CD4+ T cells. A, Cutaneous immediate hypersensitivity or AC was induced in BALB/c mice using SRW allergens. Mice were challenged with C57BL/6 corneal allografts 1 d after final exposure to SRW allergens, and allograft survival was monitored. Cutaneous allergy group (n = 10) was not significantly different from untreated control group (n = 10). p > 0.05. AC group (n = 9) was significantly different from the other two groups. p = 0.001. B, Splenic CD4+ T cells were isolated from BALB/c mice 7–10 d after they had rejected C57BL/6 corneal allografts. CD4+ T cells were cultured in the presence of BALB/c APCs that were pulsed with sonicated C57BL/6 spleen cells. Supernatants were collected 72 h later and examined for the presence of Th1 and Th2 cytokines.