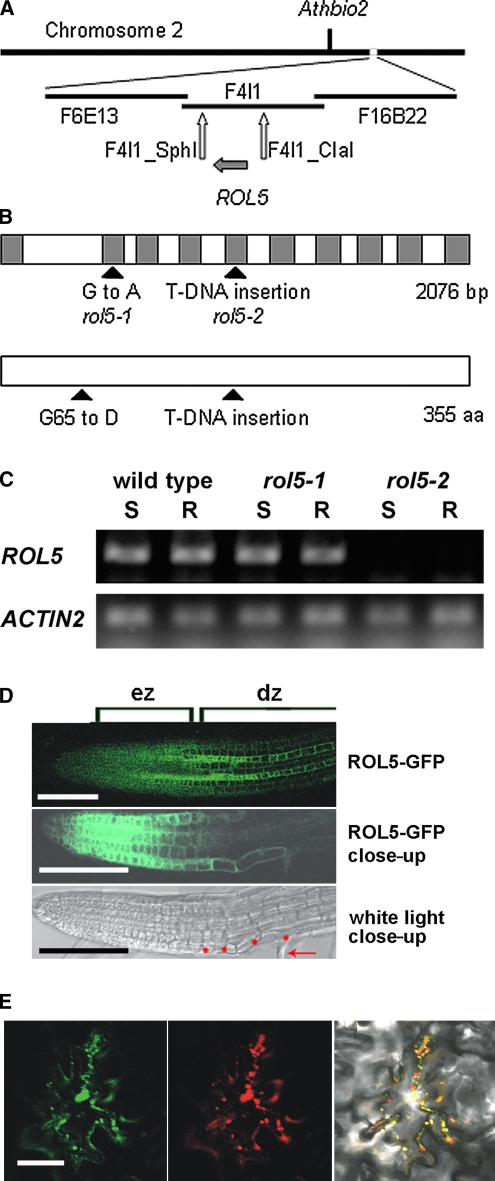
Figure 2.
Identification of the ROL5 Locus.
(A) The rol5 locus was identified by map-based cloning on the long arm of chromosome 2, south of Athbio2. BAC clones in the region of ROL5 are indicated. For mapping, cleaved-amplified polymorphic sequence and simple sequence length polymorphism markers were established, of which F4I1-Sph and F4I1-Cla were the closest flanking markers identified.
(B) The ROL5 gene consists of 10 exons encoding a protein of 355 amino acids. The G-to-A mutation in rol5-1 is located in the second exon and changes Gly-65 to Asp. rol5-2 represents a T-DNA insertion line that interrupts the reading frame at the amino acid codon Glu-170. Gray boxes, exons.
(C) RT-PCR experiments on RNA isolated from shoots (S) and roots (R) of 1-week-old seedlings demonstrated that the ROL5 gene is expressed in the wild type and the rol5-1 mutant but not to detectable levels in rol5-2. RT-PCR on the ACTIN2 gene was performed to confirm the use of similar amounts of RNA in the different samples. One of two biological replicates is shown.
(D) In roots, ROL5 is predominantly expressed in the elongation zone (ez) and in a striped pattern in the differentiation zone (dz) (top panel). A close-up of the root (GFP fluorescence in the middle panel; bright field in the bottom panel) revealed overlapping GFP fluorescence and root hair formation. Red dots, root hair–forming trichoblasts; arrow, root hair structure. Bar = 0.3 mm.
(E) When transiently expressed in Arabidopsis epidermal cells, ROL5-GFP (left panel) and a mitochondrial marker protein (for details, see Methods) fused to red fluorescent protein (middle panel) display overlapping fluorescence patterns (right panel). Bar = 50 μm.