Figure 2.
HopF2 Function Is Linked to the Inhibition of MAP Kinase Cascades.
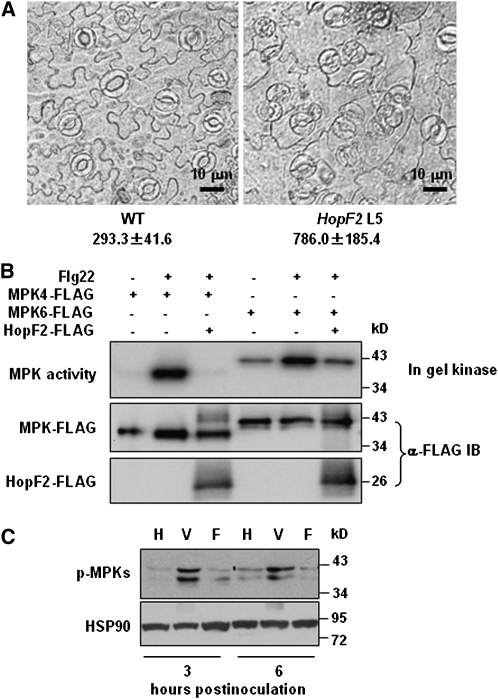
(A) HopF2 transgenic plants display clustered stomatal cells. The micrographs of the abaxial epidermis were taken 2 weeks after germination on plates containing estradiol. Numbers below the photographs are stomatal density/mm2 in HopF2 and wild-type (WT) plants, which are significantly different at a P value <0.01 (Student's t test). The results shown are representative of four independent experiments.
(B) HopF2 inhibits flg22-induced activation of MPK4 and MPK6. Protoplasts were transfected with the MPK4-FLAG or MPK6-FLAG construct in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the HopF2-FLAG construct, treated with water (−) or 1 μM flg22 (+) for 10 min, and the total protein extract was subjected to anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation. The purified MPK4-FLAG and MPK6-FLAG protein was then subjected to an in-gel kinase assay using myelin basic protein as a substrate and anti-FLAG immunoblot analysis.
(C) Bacterial PAMP-induced MAPK activation is suppressed by TTSS-delivered HopF2. Leaves of 6-week-old Col-0 plants were infiltrated with the indicated bacteria at 1 × 107 cells/mL. Leaf total protein was extracted at the indicated time points and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antiphospho-ERK antibodies. H, water control; V, P. fluorescens strain (pLN1965) bacteria lacking effector genes but containing an empty vector; F, P. fluorescens strain (pLN1965) carrying the ShcF-HopF2 construct. Equal loading was indicated by immunoblot with anti-HSP90 antibodies.