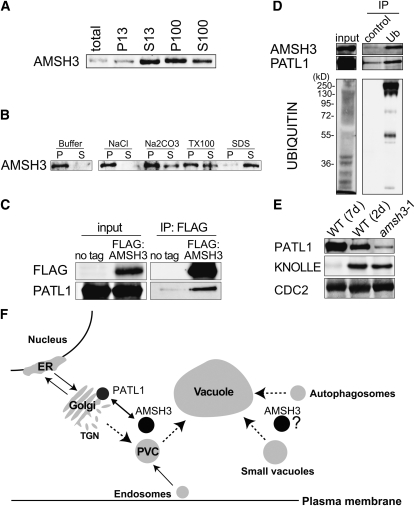
Figure 6.
AMSH3 Is a Membrane-Associated Protein That Interacts with PATL1.
(A) Immunoblots of total protein extracts after differential centrifugation. The low-speed pellet (P13) and supernatant (S13) and the high-speed pellet (P100) and supernatant (S100) were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-AMSH3 antibody.
(B) The P100 fraction obtained in (A) was incubated with the buffers containing one of 1 M NaCl, 0.1 M Na2CO3, 1% Triton X-100, or 1% SDS, and solubilization of AMSH3 was analyzed using anti-AMSH3. P, pellet; S, supernatant.
(C) Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation from 7-d-old Arabidopsis wild-type seedlings (no tag) or seedlings expressing FLAG:AMSH3. Total extracts (input) and immunoprecipitates (IP) were subjected to immunoblot using anti-FLAG and anti-PATL1 antibodies.
(D) Ubiquitin immunoprecipitation using an anti-ubiquitin P4D1-conjugated agarose (Ub) or a control ProteinA/G-agarose immunoprecipitation (control) from 7-d-old seedlings expressing AMSH3-AXA. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot using anti-AMSH3, anti-PATL1, and anti-ubiquitin antibodies.
(E) Immunoblot with an anti-PATL1 antibody on total extracts of amsh3-1 in comparison with 7- and 2-d-old wild-type seedlings. Note that the amount of PATL1 is reduced in the amsh3 mutant, whereas the amount of the cell plate protein KNOLLE is unaltered.
(F) Model of AMSH3 interactions. Protein–protein interaction data suggest a role for AMSH3 in intracellular transport involving the SEC14-homolog PATL1. AMSH3 dysfunction results in the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and defects in intracellular vesicle transport. Dotted lines mark the pathways for which AMSH3 function may be required. PVC, prevacuolar compartment; TGN, trans-Golgi network.