Figure 9.
The Interaction of Sho1 and Kpp6 Influences Pathogenicity.
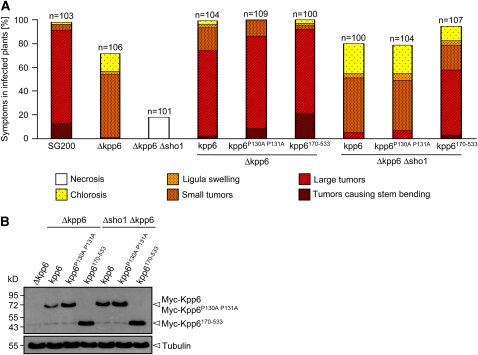
(A) Wild-type kpp6, kpp6P130A P131A, and N-terminally truncated kpp6Δ1-169 were constitutively expressed as N-terminal Myc-fusion proteins in either SG200Δkpp6 or SG200Δsho1 Δkpp6. The SG200 derivatives listed below each column were inoculated into maize seedlings, and symptoms were scored 12 d after infection as described in the legend to Figure 2.
(B) The indicated SG200Δkpp6- and SG200Δsho1 Δkpp6-derived strains were grown in liquid YEPSL to an OD600 of 1.0, and proteins were extracted and subjected to SDS-PAGE. After blotting, anti-Myc was used to detect Myc-Kpp6 as well as its mutated and truncated alleles (top panel). The Myc antibody detects with low signal intensity one unspecific cross-hybridizing protein at the size of Myc-Kpp6Δ1-169 that was disregarded. Tubulin served as loading control and was detected with antitubulin (bottom panel). The fusion proteins and tubulin are indicated by arrowheads on the right. The molecular mass marker is depicted on the left.