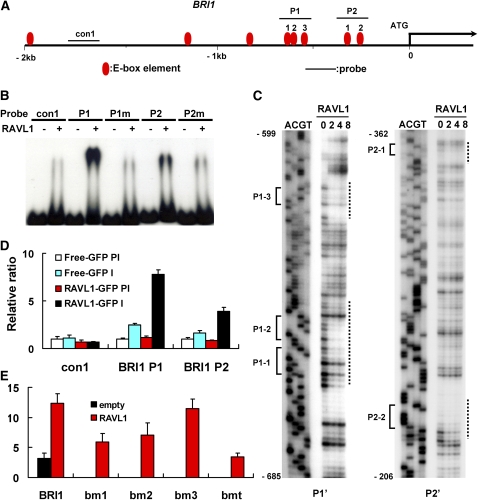
Figure 4.
In Vitro and in Vivo Assays of RAVL1 Affinity to E-Boxes of the BRI1 Promoter.
(A) The schematic indicates the locations of the E-box candidate elements and of the probes used in the EMSA, DNase I footprinting, and ChIP assays. E-box elements used for the assays are numbered as P1-1, -2, -3, P2-1, and P2-2.
(B) EMSAs for the BRI1 promoter were performed with P1, P2, and their mutated forms (P1m and P2m).
(C) DNase I footprinting assays were performed with radiolabeled P1' and P2' DNA fragments slightly shorter than P1 and P2, respectively. Lanes 0, 2, 4, and 8 indicate the amount (μg) of RAVL1 proteins added to reactions. Lanes A, C, G, and T are Maxam-Gilbert chemical sequencing lanes. E-box elements and protected regions are indicated to the left and right of the autoradiographs, respectively.
(D) An antiserum against GFP (I) and a control preimmune serum (PI) were used for ChIP assay in rice calli expressing RAVL1-GFP. The same BRI1 regions used in the EMSA were amplified from immunoprecipitated DNA. The relative ratios of immunoprecipitated DNA were determined by qRT-PCR. Input DNA was used to normalize the data. Error bars are se of the means of three qPCR replicates.
(E) A transient expression assay was performed by cotransfection of pUbi:RAVL1 and each of the vectors expressing GUS from native and E-box-mutated BRI1 promoters. The bm1 construct is a BRI1 promoter in which two adjacent E-box motifs, P1-1 and -2, are mutated, while the bm2 and bm3 promoters carry mutations in the P1-3 and P2-1 E-boxes, respectively. The bmt promoter contains mutations in all six E-box motifs within 1 kb of the BRI1 promoter. Error bars are se of the means of three replicates.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]