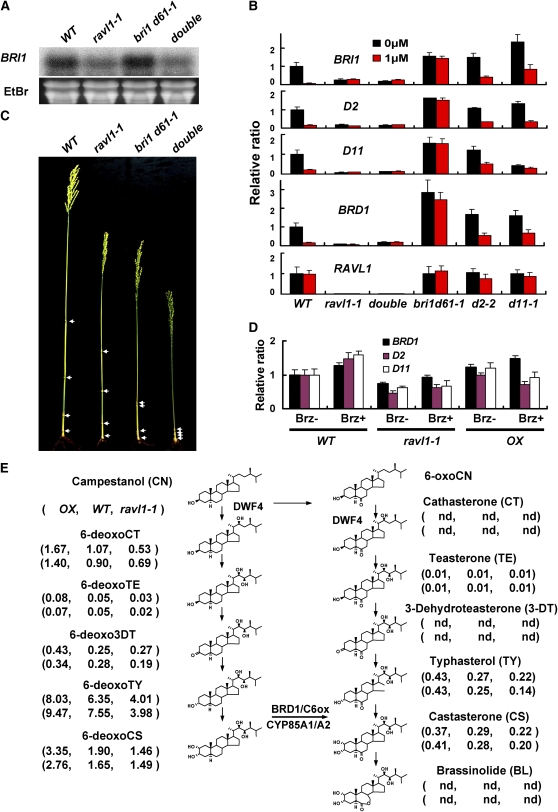
Figure 7.
Expression Relationship among RAVL1, BRI1, and Synthetic Genes and Measurement of BR Intermediates.
(A) RNA gel blot analysis of the expression levels of BRI1 in double mutants and single mutants of ravl1-1 and bri1 d61-1. WT, wild type.
(B) The effects of epiBL treatment on the expression of BRI1 and BR synthetic genes (D2, D11, and BRD1) were examined in ravl1-1, bri1 d61-1, and BR-deficient mutants. The relative ratios of mutants to the wild type without BL treatment were measured by qRT-PCR. 25S rRNA was used control to normalize the expression data. Error bars are se of the means of three qPCR replicates.
(C) Double mutants (ravl1-1 and bri1 d61-1) showed more severe dwarfism than ravl1-1 or bri1 d61-1 single mutant plants.
(D) The effects of brassinazole treatment on the expression of BR synthetic genes (BRD1, D2, and D11) were examined in the wild type, ravl1-1, and RAVL1 OX. Brz+ or Brz− indicate with or without treatment of brassinazole, respectively. The relative ratios of mutants and OX to the wild type without Brz treatment were measured by qRT-PCR. 25S rRNA was used control to normalize the expression data. Error bars are se of the means of three qPCR replicates.
(E) The concentration of various BRs was measured in shoots. The amounts of BL and its precursors are shown in the following order: OX, wild type, and ravl1-1. OX indicates RAVL1 overexpressor. BR levels were measured in two independent experiments. Units are ng/g of fresh weight of samples. **, Not detected.