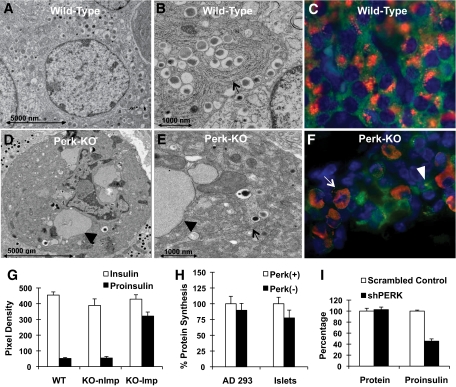
FIG. 1.
PERK-deficient mice exhibit an abnormal β-cell morphology (A–F) and normal steady-state protein synthesis (G). A: TEM image of a normal β-cell from a P1 wild-type mouse. B: At higher magnification, the normal laminar morphology of the ER and associated ribosomes can be seen in the wild-type β-cell (arrow). C: IHC image of a normal β-cell from a P1 wild-type mouse showing proinsulin (red) within the Golgi and insulin (green) throughout the cytoplasm. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Pancreata were isolated, fixed, and prepared for IHC analysis as previously described (9). D: TEM image of a Perk KO β-cell from a P1 mouse. E: At higher magnification, the overall abnormal ER morphology (arrow) and frequent ribosome-studded balloon-like structures (arrow head) can be readily detected. F: IHC staining for proinsulin in Perk KO β-cells from a P1 mouse shows a subpopulation of cells with abnormal distribution of proinsulin throughout the cytoplasm that colocalizes with ER markers (11). G: Quantitative analysis of insulin and proinsulin levels were performed on IHC images of β-cells in postnatal day 1 Perk KO and wild-type littermates. All procedures and reagents for histochemical preparation and image collection were done at the same time under identical conditions to allow direct comparison of signal density area estimates of insulin and proinsulin between genotypes and individuals. Area density analysis was performed using NIH Image J on clusters of β-cells within islets or on individual β-cells so as to exclude other endocrine cell types. Background subtraction was performed by subtracting nonspecific pixel density calculated from the adjacent exocrine pancreas. A total of 16–18 islets were analyzed for two individual littermates per genotype. To compare impacted-ER β-cells with nonimpacted-ER β-cells in Perk KO mice, 40 individual β-cells each were analyzed. Average pixel densities, after background subtraction, are shown without any form of normalization. KO Imp, Perk KO, impacted-ER phenotype; KO nImp, Perk KO, nonImpacted-ER phenotype. H: Cells were cultured in 11 mmol/l glucose prior to the addition of S35-labeled cysteine and methionine. For AD293 cells Perk (+) represents empty vector and Perk (−) represents cells impaired for Perk activity by DNPerk. For islets Perk (+) represents wild-type neonatal islets (n = 16) and Perk (−) (n = 8) represents islets isolated from neonatal Perk KO mice. Differences are not statistically significant (P > 0.05). I: Global and proinsulin synthesis was assessed in INS1 832/13 cells in which Perk was ablated by expression of shPerk as compared with a scramble control (shScram). The level of rat Perk mRNA and protein were reduced by 60–70% and 56–66%, respectively, at 48 h after the induction of the expression of shRNAs by treatment with 2 mg/ml doxycycline in INS1-832/13 β-cells. Cells were pulse-labeled with S35-labeled cysteine and methionine for 30 min, and cellular extracts were either TCA precipitated for analysis of global protein synthesis or immunoprecipitated with proinsulin antibody followed by electrophoretic separation. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)