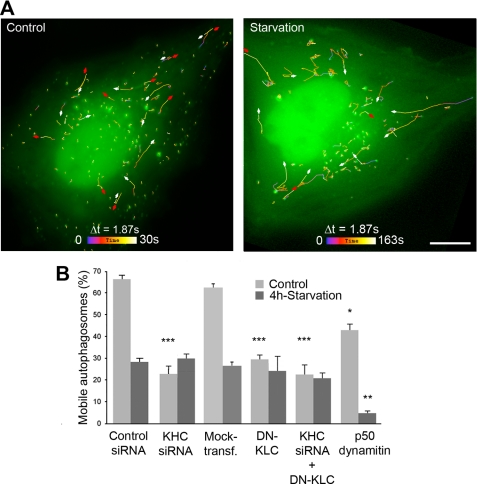
FIGURE 5.
Kinesin-1 involvement in carrying autophagosomes decreases upon starvation. A, autophagosomes exhibit centrifugal movements. HeLa cells expressing tandem fluorescent LC3 were followed in the GFP channel by time-lapse microscopy with 1.87-s intervals during the indicated periods of time. Mobile autophagosomes were tracked, and their trajectories were color-coded as indicated. Red and white arrows show centrifugal and centripetal movements, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, kinesin-1 functions to carry autophagosomes in basal conditions, whereas autophagosome mobility drops by ∼50% after nutrient deprivation. The percentage of mobile autophagosomes was measured by following tandem LC3 as shown above, without and with kinesin-1 inhibition. As kinesin-1 inhibition prevents autophagy stimulation, the proportion of cells that exhibited fluorescent puncta was ∼20% after kinesin-1 inhibition, although it reached ∼60% in control conditions. Dynein inhibition caused by p50 dynamitin overexpression was used to control that autophagosome mobility could actually be inhibited in starvation conditions. Asterisks indicate the levels of significance relative to the corresponding control measured in the same condition as follows: *** means p < 0.001; ** means p < 0.01; * means p < 0.05. Data were obtained from the examination of at least 500 autophagosomes (10 cells) in each condition of kinesin-1 inhibition.