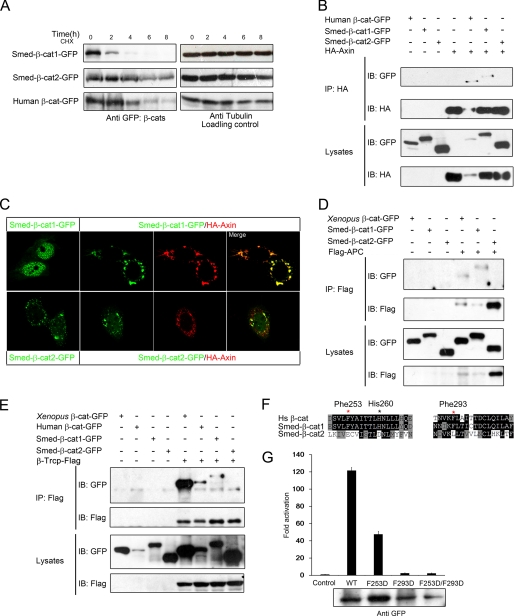
FIGURE 4.
Only Smed-β-catenin-1 is captured by the degradation complex. A, the Smed-β-catenins showed different stability in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transfected as indicated. Thirty-two hours after transfection, cycloheximide (CHX) was added to the culture medium at a final concentration of 100 μg/ml. Cell lysates were collected every 2 h thereafter and analyzed by Western blot. Whereas Smed-β-catenin-2 remained relatively stable for up to 8 h, Smed-β-catenin-1 was hardly detectable after only 4 h. B, co-IP assays with Axin reveal an interaction with Smed-β-catenin-1 but not Smed-β-catenin-2. C, localization of Smed-β-catenins alone or co-expressed with Axin in HeLa cells. D and E, co-IP with APC and β-Trcp reveals an interaction with Smed-β-catenin-1 but not Smed-β-catenin-2. Human APC fragment (amino acids 958–1287) and full-length β-Trcp were used in the assays. Human and Xenopus β-catenins were used as positive controls. F, alignments of the amino acid sequences from human β-catenin and Smed-β-catenins. Critical residues for β-catenin to interact with Axin, APC, and TCF are shown. Red star, important residues in the hydrophobic pocket; black star, residue for hydrogen bond. G, Super-TOPflash reporter assay following co-transfection of HEK293T cells with reporter plasmids and 90 ng of wild type Smed-β-catenin-1 or its mutations. The protein expression level is shown below. IB, immunoblot; HA, hemagglutinin.