FIGURE 1.
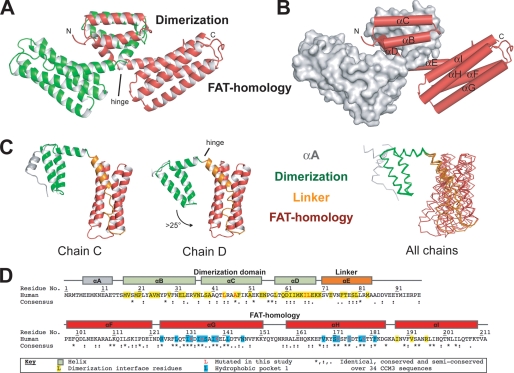
Overall structure of CCM3. A, scheme representation of the CCM3 dimer. The CCM3 dimerization (Dimerization) domain and FAT-homology (FAT-homology) domains are indicated. The location of the hinge between the domains is indicated. B, same orientation as panel A showing one chain as a gray surface and helices αB to αI indicated. C, five solved CCM3 chains hinge around residues Lys-69–Lys-70. Chains C and D of the P212121 crystal form show the largest hinge angle difference and are shown. Backbone trace for all five chains from both crystal forms is superposed on the N-terminal dimerization domain. αA, gray; dimerization domain, green; αE and loop EF, orange; FAT-homology domain, red. D, sequence and secondary structure assignments of human CCM3. Human sequence (Swiss-Prot Q9BUL8) and residue numbers with secondary structure assignment are for helices αA through αI and colored per domain as in panel B. Residues involved in dimerization are colored yellow and the hydrophobic pocket 1 (HP1) in blue. The consensus sequence over 34 CCM3 sequences from human to Drosophila by ClustalW is shown. (*) indicates identical; (:), highly conserved; (.), semi-conserved (see supplemental Fig S4B for complete alignment). Residues mutated in this study are colored red. All structure figures are made with Pymol.