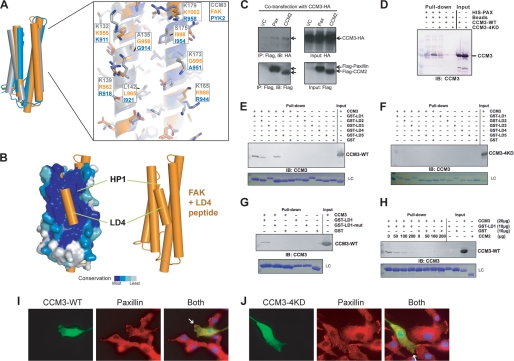
FIGURE 4.
CCM3 binds the LD-motif region of paxillin. A, left, superposition of CCM3, Pyk2, and FAK as shown in Fig. 3A. Right, Pyk2 colored blue (PDB ID: 3GM1) (22), FAK in orange (PDB ID: 1OW7) (23), and CCM3 (gray). Residues are labeled for comparison. B, superposition of FAK FAT domain bound to paxillin LD4 peptide (PDB ID: 1OW7) (23) with CCM3 FAT-homology domain suggests that CCM3 can bind LD-motifs. C, CCM3 co-immunoprecipitation with CCM2 or paxillin. Full-length CCM3-HA and either full-length Flag-CCM2, full-length Flag-paxillin or vector control (VC) were co-transfected into 293T cells. CCM3 immunoprecipitates both Flag-CCM2 and Flag-paxillin. D, N-terminal 6×His-tagged paxillin-(1–321) pull-down CCM3, but not CCM3–4KD. E–G, CCM3 pull-downs with paxillin. E, GST fusions of paxillin LD-motifs (24, 25) pull-down full-length CCM3. LC, Coomassie-stained loading control for GST-LD motifs. F, quadruple mutation of conserved lysines in CCM3, K132D, K139D, K172D, and K179D (CCM3–4KD) renders CCM3 unable to pull-down with paxillin LD-motifs. G, mutation of paxillin LD1, LL7,8RR, prevents CCM3 pull-down. H, competition. CCM2 and paxillin compete to bind CCM3. Constant GST-LD1 bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads was incubated with constant CCM3 and increasing CCM2 PTB domain. CCM2 PTB domain competes with GST-LD1 for binding to CCM3. I and J, immunofluorescence. Full-length CCM3 (I) or CCM3–4KD (J) were transfected into BAECs. Transfected CCM3 and endogenous paxillin were detected by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy with anti-Flag (rabbit; for CCM3) and anti-paxillin (mouse), followed by FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit and TRITC-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibodies. CCM3 partially co-localizes with endogenous paxillin at the leading edges of migrating cells. Localization of overexpressed CCM3–4KD to leading edges is reduced (indicated with white arrows).