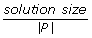Table 2.
Solutions for proteome datasets
| Proteome | length | IP | Greedy | |A| | |P| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | 4-5 | 2,020 (10.1%) | 2,292 (11.5%) | 527,164 | 20,010 |
| Mus musculus | 4-5 | 1,541 (9.6%) | 1,727 (10.8%) | 473,406 | 15,995 |
| Rattus norvegicus | 4-5 | 851 (11.7%) | 970 (13.3%) | 273,558 | 7,295 |
| Bos taurus | 4-5 | 790 (14.2%) | 903 (16.1%) | 199,735 | 5,584 |
| Saccharomyces cervisiae | 4-5 | 1,000 (15.6%) | 1,134 (17.6%) | 240,253 | 6,422 |
| Homo sapiens | 4 | 2,026 (10.1%) | 2,306 (11.5%) | 86,963 | 19,979 |
| Mus musculus | 4 | 1,529 (9.6%) | 1,737 (10.9%) | 83,073 | 15,974 |
| Rattus norvegicus | 4 | 858 (11.8%) | 975 (13.4%) | 64,058 | 7,294 |
| Bos taurus | 4 | 792(14.2%) | 896 (16.1%) | 53,751 | 5,576 |
| Saccharomyces cervisiae | 4 | 995 (15.5%) | 1,130 (17.6%) | 58,464 | 6,405 |
Comparison of the solution quality of the integer program IP (CPLEX solver, running time limited to 12 hours) and the greedy set cover algorithm on proteomes of different species, and epitope length settings. |A| denotes the number of different epitopes, |P| the number of target proteins, the percentage next to solution sizes is the coverage score