Figure 6.
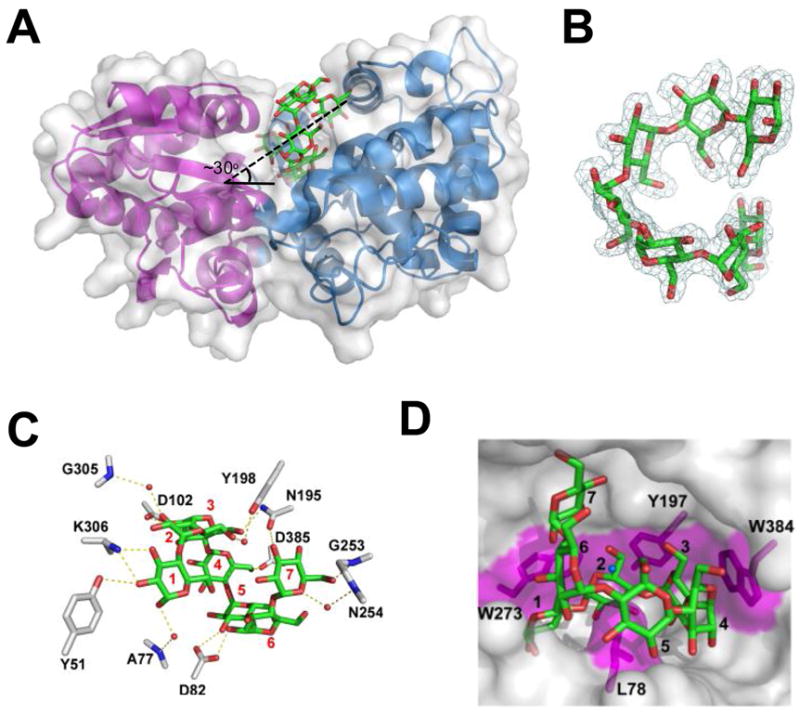
The three-dimensional structure of MalX in complex with maltohepatose at 2.0 Å resolution. A) MalX is shown from a side projection in a ribbon format with the small N-terminal domain colored purple and the large C-terminal domain colored blue. The solvent accessible surface is shown in transparent grey and maltohepatose is shown as green sticks. The approximate angle of the entry for the sugar is indicated. B) Electron density of maltohepatose shown as a maximum-likelihood (Murshudov et al., 1997)/σa-weighted (Read, 1986) 2Fobs-Fcalc electron density map contoured at 1.0 σ (0.28e−/Å3). C) Direct and water-mediated hydrogen bonds within the binding site of MalX. Side chains are represented as grey sticks, maltoheptaose as green sticks, and waters as red spheres. The binding subsites are labelled. D) Solvent accessible surface representation of the binding site. Putative hydrophobic interactions, including the three “stacking” interactions and a leucine “pin,” are shaded in magenta. The ligand subsites are numbered as in (C).
