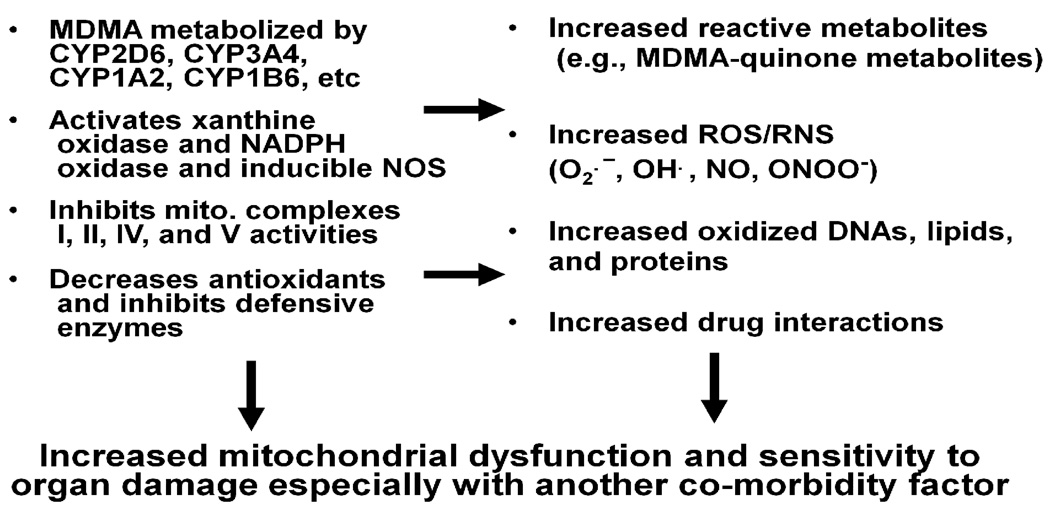
Fig. 1.
MDMA-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress and functional consequences. Hepatic metabolism of MDMA and activation of other enzymes contribute to increased ROS/RNS production and reduced levels of anti-oxidants. These changes promote oxidative modifications of many mitochondrial proteins, resulting in their inactivation followed by mitochondrial dysfunction and tissue damage after MDMA exposure.